H. P. Lovecraft
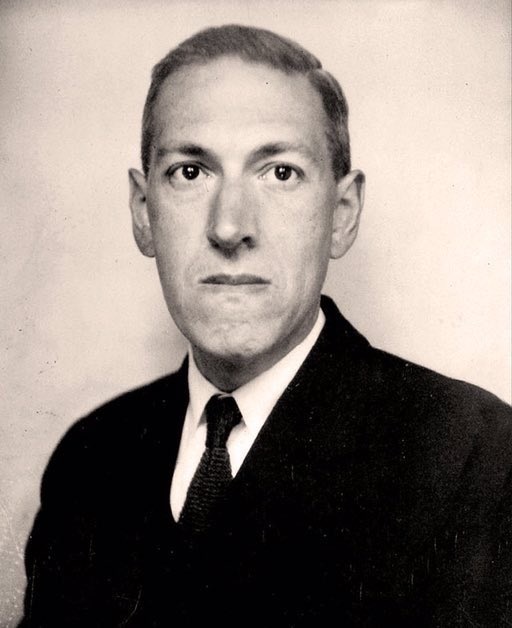
Howard Phillips Lovecraft (August 20, 1890 – March 15, 1937) was an American writer of weird, science, fantasy, and horror fiction. He is best known for his creation of the Cthulhu Mythos.
Early life
Lovecraft was born in his family home on August 20, 1890, in Providence, Rhode Island. He was the only child of Winfield Scott Lovecraft and Sarah Susan (née Phillips) Lovecraft. Susie's family was of substantial means at the time of their marriage, as her father, Whipple Van Buren Phillips, was involved in business ventures. In April 1893, after a psychotic episode in a Chicago hotel, Winfield was committed to Butler Hospital in Providence. His medical records state that he had been "doing and saying strange things at times" for a year before his commitment and he ultimately died of late-stage syphilis.
After his father's institutionalization, his grandfather Whipple became a father figure to Lovecraft. Whipple, who often traveled to manage his business, maintained correspondence by letter with the young Lovecraft who, by the age of three, was already proficient at reading and writing. In his old age, he helped raise the young H. P. Lovecraft and educated him not only in the classics, but also in original weird tales of "winged horrors" and "deep, low, moaning sounds" which he created for his grandchild's entertainment.
Lovecraft's earliest known literary works were written at the age of seven, and were poems restyling the Odyssey and other Greco-Roman mythological stories. Lovecraft would later write that during his childhood he was fixated on the Greco-Roman pantheon, and briefly accepted them as genuine expressions of divinity, foregoing his Christian upbringing. He recalled, at five years old, being told Santa Claus did not exist and retorted by asking why "God is not equally a myth?"
In the spring of 1904, Whipple's largest business venture suffered a catastrophic failure. Within months, he died at age 70 due to a stroke. After Whipple's death, Susie was unable to financially support the upkeep of the expansive family home on what remained of the Phillips' estate. Later that year, she was forced to move to a small duplex with her son. Lovecraft called this time one of the darkest of his life, remarking in a 1934 letter that he saw no point in living anymore; he considered the possibility of committing suicide. His scientific curiosity and desire to know more about the world prevented him from doing so. It was also during this period that Lovecraft produced the first of the fictional works that he would later be known for, namely "The Beast in the Cave" and "The Alchemist."
Though Lovecraft maintained that he was going to attend Brown University after high school, after leaving school due to a mysterious medical ailment in 1908, he never graduated and never attended school again.
Career as an author
In 1916, Lovecraft published his first short story, "The Alchemist," in the main United Amateur Press Association (UAPA) journal, which was a departure from his usual verse. Due to the encouragement of W. Paul Cook, another UAPA member and future lifelong friend, Lovecraft began writing and publishing more prose fiction. Soon afterwards, he wrote "The Tomb" and "Dagon." "The Tomb," by Lovecraft's own admission, was greatly influenced by the style and structure of Edgar Allan Poe's works. Meanwhile, "Dagon" is considered Lovecraft's first work that displays the concepts and themes that his writings would later become known for.
Late 1919 saw Lovecraft become more outgoing. After a period of isolation, he began joining friends in trips to writer gatherings; the first being a talk in Boston presented by Lord Dunsany, whom Lovecraft had recently discovered and idolized. In early 1920, at an amateur writer convention, he met Frank Belknap Long, who would end up being Lovecraft's most influential and closest confidant for the remainder of his life. The influence of Dunsany is apparent in his 1919 output, which is part of what would be called Lovecraft's Dream Cycle, including "The White Ship" and "The Doom That Came to Sarnath."
It was later in 1920 that Lovecraft began publishing the earliest Cthulhu Mythos stories. The Cthulhu Mythos, a term coined by later authors, encompasses Lovecraft's stories that share a commonality in the revelation of cosmic insignificance, initially realistic settings, and recurring entities and texts. The prose poem "Nyarlathotep" and the short story "The Crawling Chaos", in collaboration with Winifred Virginia Jackson, were written in late 1920. Following in early 1921 came "The Nameless City," the first story that falls definitively within the Cthulhu Mythos. In it is one of Lovecraft's most enduring phrases, a couplet recited by Abdul Alhazred; "That is not dead which can eternal lie; And with strange aeons even death may die."
Move to New York and Weird Tales
Lovecraft married Sonia Greene on March 3, 1924, and relocated to her Brooklyn apartment at 259 Parkside Avenue; she thought he needed to leave Providence to flourish and was willing to support him financially. Greene, who had been married before, later said Lovecraft had performed satisfactorily as a lover, though she had to take the initiative in all aspects of the relationship. She attributed Lovecraft's passive nature to a stultifying upbringing by his mother.
He was enthralled by New York, and, in what was informally dubbed the Kalem Club, he acquired a group of encouraging intellectual and literary friends who urged him to submit stories to Weird Tales. Its editor, Edwin Baird, accepted many of Lovecraft's stories for the ailing publication, including "Under the Pyramids," which was ghostwritten for Harry Houdini.
Not long after the marriage, Greene lost her business and her assets disappeared in a bank failure. Lovecraft made efforts to support his wife through regular jobs, but his lack of previous work experience meant he lacked proven marketable skills. The publisher of Weird Tales was attempting to turn the loss-making magazine profitable again and offered the job of editor to Lovecraft, who declined, citing his reluctance to relocate to Chicago on aesthetic grounds.
In August 1925, he wrote "The Horror at Red Hook" and "He," in the latter of which the narrator says "My coming to New York had been a mistake; for whereas I had looked for poignant wonder and inspiration [...] I had found instead only a sense of horror and oppression which threatened to master, paralyze, and annihilate me." Around this time he wrote the outline for "The Call of Cthulhu," with its theme of the insignificance of all humanity. With a weekly allowance Greene sent, Lovecraft moved to a working-class area of Brooklyn Heights, where he resided in a tiny apartment. He had lost approximately 40 pounds (18 kg) of body weight by 1926, when he returned to Providence.
Final years in Providence
Back in Providence, Lovecraft lived with his aunts in a "spacious brown Victorian wooden house" at 10 Barnes Street until 1933. He then moved to 66 Prospect Street, which would become his final home. The period beginning after his return to Providence contains some of his most prominent works, including The Dream-Quest of Unknown Kadath, The Case of Charles Dexter Ward, "The Call of Cthulhu" and The Shadow over Innsmouth. After returning, he began to engage in antiquarian travels across the eastern seaboard during the summer months.
Later, in August, Robert E. Howard wrote a letter to Weird Tales praising a then-recent reprint of H. P. Lovecraft's "The Rats in the Walls" and discussing some of the Gaelic references used within. Editor Farnsworth Wright forwarded the letter to Lovecraft, who responded positively to Howard, and soon the two writers were engaged in a vigorous correspondence that would last for the rest of Howard's life. Howard quickly became a member of the Lovecraft Circle, a group of writers and friends all linked through Lovecraft's voluminous correspondence, as he introduced his many like-minded friends to one another and encouraged them to share their stories, utilize each other's fictional creations, and help each other succeed in the field of pulp fiction.
Meanwhile, Lovecraft was increasingly producing work that brought him no remuneration. Affecting a calm indifference to the reception of his works, Lovecraft was in reality extremely sensitive to criticism and easily precipitated into withdrawal. He was known to give up trying to sell a story after it had been once rejected. Sometimes, as with The Shadow over Innsmouth, he wrote a story that might have been commercially viable but did not try to sell it. Lovecraft even ignored interested publishers. He failed to reply when one inquired about any novel Lovecraft might have ready: although he had completed such a work, The Case of Charles Dexter Ward, it was never typed up. A few years after Lovecraft had moved to Providence, he and his wife Sonia Greene, having lived separately for so long, agreed to an amicable divorce. Greene moved to California in 1933 and remarried in 1936, unaware that Lovecraft, despite his assurances to the contrary, had never officially signed the final decree.
In late 1936, he witnessed the publication of The Shadow over Innsmouth as a paperback book. 400 copies were printed, and the work was advertised in Weird Tales and several fan magazines. However, Lovecraft was displeased, as this book was riddled with errors that required extensive editing. It sold slowly and only approximately 200 copies were bound. The remaining 200 copies were destroyed after the publisher went out of business for the next seven years. By this point, Lovecraft's literary career was reaching its end. Shortly after having written his last original short story, "The Haunter of the Dark," he stated that the hostile reception of At the Mountains of Madness had done "more than anything to end my effective fictional career." His declining psychological and physical states made it impossible for him to continue writing fiction.
Death
As his literary career came to an end, Lovecraft's physical health was deteriorating. Due to his fear of doctors, he was not examined until a month before his death. After seeing a doctor, he was diagnosed with terminal cancer of the small intestine. He remained hospitalized until he died. He lived in constant pain until his death on March 15, 1937, in Providence.
In accordance with his lifelong scientific curiosity, he kept a diary of his illness until he was physically incapable of holding a pen. Lovecraft was listed along with his parents on the Phillips family monument. In 1977, fans erected a headstone in Swan Point Cemetery on which they inscribed his name, the dates of his birth and death, and the phrase "I AM PROVIDENCE"—a line from one of his personal letters.
Legacy
Lovecraft was relatively unknown during his lifetime. While his stories appeared in prominent pulp magazines such as Weird Tales, not many people knew his name. He did, however, correspond regularly with other contemporary writers such as Clark Ashton Smith and August Derleth, who became his friends, even though he never met them in person. This group became known as the "Lovecraft Circle", since their writings freely borrowed Lovecraft's motifs, with his encouragement.
After Lovecraft's death, the Lovecraft Circle carried on. August Derleth founded Arkham House with Donald Wandrei to preserve Lovecraft's works and keep them in print. He added to and expanded on Lovecraft's vision, not without controversy. While Lovecraft considered his pantheon of alien gods a mere plot device, Derleth created an entire cosmology, complete with a war between the good Elder Gods and the evil Outer Gods, such as Cthulhu and his ilk. The forces of good were supposed to have won, locking Cthulhu and others beneath the earth, the ocean, and elsewhere. Derleth's Cthulhu Mythos stories went on to associate different gods with the traditional four elements of fire, air, earth, and water, which did not line up with Lovecraft's original vision of his mythos. However, Derleth's ownership of Arkham House gave him a position of authority in Lovecraftiana that would not dissipate until his death, and through the efforts of Lovecraft scholars in the 1970s.
Lovecraft's works have influenced many writers and other creators. Stephen King has cited Lovecraft as a major influence on his works. As a child in the 1960s, he came across a volume of Lovecraft's works which inspired him to write his fiction. He goes on to argue that all works in the horror genre that were written after Lovecraft were influenced by him. In the field of comics, Alan Moore has described Lovecraft as having been a formative influence on his graphic novels. Film director John Carpenter's films include direct references and quotations of Lovecraft's fiction, in addition to their use of a Lovecraftian aesthetic and themes. Guillermo del Toro has been similarly influenced by Lovecraft's corpus.
Influence on occultism
Several contemporary religions have been influenced by Lovecraft's works. Kenneth Grant, the founder of the Typhonian Order, incorporated Lovecraft's Mythos into his ritual and occult system. Grant combined his interest in Lovecraft's fiction with his adherence to Aleister Crowley's Thelema. The Typhonian Order considers Lovecraftian entities to be symbols through which people may interact with something inhuman.[ Grant also argued that Crowley himself was influenced by Lovecraft's writings, particularly in the naming of characters in The Book of the Law. Similarly, The Satanic Rituals, co-written by Anton LaVey and Michael A. Aquino, includes the "Ceremony of the Nine Angles," which is a ritual that was influenced by the descriptions in "The Dreams in the Witch House." It contains invocations of several of Lovecraft's fictional gods.
There have been several books that have claimed to be an authentic edition of Lovecraft's Necronomicon. The Simon Necronomicon is one such example. It was written by an unknown figure who identified themselves as "Simon." Peter Levenda, an occult author who has written about the Necronomicon, claims that he and "Simon" came across a hidden Greek translation of the grimoire while looking through a collection of antiquities at a New York bookstore during the 1960s or 1970s. This book was claimed to have borne the seal of the Necronomicon. Levenda went on to claim that Lovecraft had access to this purported scroll. A textual analysis has determined that the contents of this book were derived from multiple documents that discuss Mesopotamian myth and magic. The finding of a magical text by monks is also a common theme in the history of grimoires. It has been suggested that Levenda is the true author of the Simon Necronomicon.
Copyright status
Despite several claims to the contrary, there is currently no evidence that any company or individual owns the copyright to any of Lovecraft's works, and it is generally accepted that it has passed into the public domain.
Searches of the Library of Congress have failed to find any evidence that these copyrights were renewed after the 28-year period, making it likely that these works are in the public domain. However, the Lovecraft literary estate, reconstituted in 1998 under Robert C. Harrall, has claimed that they own the rights. They have been based in Providence since 2009 and have been granting the rights to Lovecraft's works to several publishers. Their claims have been criticized by scholars, such as Chris J. Karr, who has argued that the rights had not been renewed.