Difference between revisions of "Template:Occult.live:Today's featured article"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) |
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) |
||
| (115 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
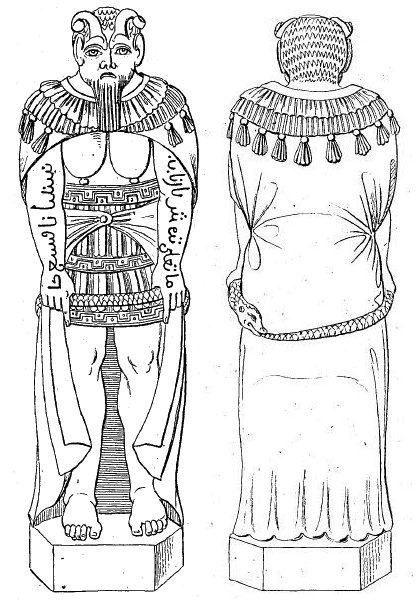
[[File: | [[File:Goat of Mendes Statue.png|200px|left]] | ||
'''[[ | '''[[Baphomet]]''' is a deity allegedly worshipped by the [[Knights Templar]] that subsequently became incorporated into various [[occult]] and Western esoteric traditions. The name "Baphomet" appeared in trial transcripts for the [[Inquisition]] of the Knights Templar starting in 1307, but it did not enter popular English usage until the 19th century during debate and speculation on the reasons for the suppression of the Templar order. Baphomet is a symbol of balance in occult traditions, the origin of which some [[occultist]]s have linked with the [[Gnosticism|Gnostics]] and Templars; although Baphomet is also revered as a deity or a [[demon]]. Since 1856 the figure of Baphomet has been associated with the "Sabbatic Goat" image drawn by [[Éliphas Lévi]]. | ||
'''([[Baphomet|Full Article...]])''' | |||
'''([[ | |||
Latest revision as of 22:05, 1 January 2026
Baphomet is a deity allegedly worshipped by the Knights Templar that subsequently became incorporated into various occult and Western esoteric traditions. The name "Baphomet" appeared in trial transcripts for the Inquisition of the Knights Templar starting in 1307, but it did not enter popular English usage until the 19th century during debate and speculation on the reasons for the suppression of the Templar order. Baphomet is a symbol of balance in occult traditions, the origin of which some occultists have linked with the Gnostics and Templars; although Baphomet is also revered as a deity or a demon. Since 1856 the figure of Baphomet has been associated with the "Sabbatic Goat" image drawn by Éliphas Lévi.