Difference between revisions of "Set"
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) (Created page with "300px|thumb|The Egyptian God Set '''Set''' (/sɛt/; Egyptological: ''Sutekh'' - ''swtẖ'' ~ ''stẖ'' or Greek: '''Seth''' /sɛθ/) is a god of deserts, stor...") |
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
In a legend in the [[Pyramid Texts]], as punishment for his rebellion and overthrow of Osiris, Set was transformed into a sacrificial red ox (some legends say a red goat). His foreleg (''xpS'') was cut off and thrown into the sky where it became Meskhetiu (''Msxtyw''), a group of seven stars in the northern sky (likely either Ursa Major or Ursa Minor). | In a legend in the [[Pyramid Texts]], as punishment for his rebellion and overthrow of Osiris, Set was transformed into a sacrificial red ox (some legends say a red goat). His foreleg (''xpS'') was cut off and thrown into the sky where it became Meskhetiu (''Msxtyw''), a group of seven stars in the northern sky (likely either Ursa Major or Ursa Minor). | ||
The foreleg was not only a protective god, but it was also a lasting symbol of power and strength, especially of strength in the afterlife. Thousands of blue or red foreleg | The foreleg was not only a protective god, but it was also a lasting symbol of power and strength, especially of strength in the afterlife. Thousands of blue or red foreleg [[amulet]]s have been found wrapped in the bandages of mummies across all periods of Egyptian history, and drawings of ''Msxtyw'' feature prominently alongside the [[Egyptian decans|decanal stars]] in the Middle Kingdom Period coffins. | ||
During the Old Kingdom Period, it was common for the Pharaoh to wrestle a red ox in public to display his physical prowess and fitness to rule over the land. The foreleg of the defeated ox was severed and consumed as a symbol of his continued strength. | During the Old Kingdom Period, it was common for the Pharaoh to wrestle a red ox in public to display his physical prowess and fitness to rule over the land. The foreleg of the defeated ox was severed and consumed as a symbol of his continued strength. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
In a key episode in the conflict, Set rapes Horus. Set's violation is partly meant to degrade his rival, but it also involves homosexual desire, in keeping with one of Set's major characteristics, his forceful, potent, and indiscriminate sexuality. In the earliest account of this episode, in a fragmentary Middle Kingdom papyrus, the sexual encounter begins when Set asks to have sex with Horus, who agrees on the condition that Set will give Horus some of his strength. The encounter puts Horus in danger, because in Egyptian tradition semen is a potent and dangerous substance, akin to poison. According to some texts, Set's semen enters Horus's body and makes him ill, but in "Contendings", Horus thwarts Set by catching Set's semen in his hands. Isis retaliates by putting Horus's semen on lettuce-leaves that Set eats. Set's defeat becomes apparent when this semen appears on his forehead as a golden disk. He has been impregnated with his rival's seed and as a result "gives birth" to the disk. In "Contendings," Thoth takes the disk and places it on his own head; in earlier accounts, it is Thoth who is produced by this anomalous birth. | In a key episode in the conflict, Set rapes Horus. Set's violation is partly meant to degrade his rival, but it also involves homosexual desire, in keeping with one of Set's major characteristics, his forceful, potent, and indiscriminate sexuality. In the earliest account of this episode, in a fragmentary Middle Kingdom papyrus, the sexual encounter begins when Set asks to have sex with Horus, who agrees on the condition that Set will give Horus some of his strength. The encounter puts Horus in danger, because in Egyptian tradition semen is a potent and dangerous substance, akin to poison. According to some texts, Set's semen enters Horus's body and makes him ill, but in "Contendings", Horus thwarts Set by catching Set's semen in his hands. Isis retaliates by putting Horus's semen on lettuce-leaves that Set eats. Set's defeat becomes apparent when this semen appears on his forehead as a golden disk. He has been impregnated with his rival's seed and as a result "gives birth" to the disk. In "Contendings," Thoth takes the disk and places it on his own head; in earlier accounts, it is Thoth who is produced by this anomalous birth. | ||
Another important episode concerns mutilations that the combatants inflict upon each other: Horus injures or steals Set's testicles and Set damages or tears out one, or occasionally both, of Horus's eyes. Sometimes the eye is torn into pieces. Set's mutilation signifies a loss of virility and strength. The removal of Horus's eye is even more important, for this stolen eye of Horus represents a wide variety of concepts in Egyptian religion. One of Horus's major roles is as a sky deity, and for this reason his right eye was said to be the sun and his left eye the moon. The theft or destruction of the eye of Horus is therefore equated with the darkening of the moon in the course of its cycle of phases, or during eclipses. Horus may take back his lost Eye, or other deities, including Isis, Thoth, and Hathor, may retrieve or heal it for him. | Another important episode concerns mutilations that the combatants inflict upon each other: Horus injures or steals Set's testicles and Set damages or tears out one, or occasionally both, of Horus's eyes. Sometimes the eye is torn into pieces. Set's mutilation signifies a loss of virility and strength. The removal of Horus's eye is even more important, for this stolen eye of Horus represents a wide variety of concepts in Egyptian religion. One of [[Horus]]'s major roles is as a sky deity, and for this reason his right eye was said to be the sun and his left eye the moon. The theft or destruction of the eye of Horus is therefore equated with the darkening of the moon in the course of its cycle of phases, or during eclipses. Horus may take back his lost Eye, or other deities, including [[Isis]], [[Thoth]], and [[Hathor]], may retrieve or heal it for him. | ||
Egyptologist Herman te Velde argues that the tradition about the lost testicles is a late variation on Set's loss of semen to Horus, and that the moon-like disk that emerges from Set's head after his impregnation is the Eye of Horus. If so, the episodes of mutilation and sexual abuse would form a single story, in which Set assaults Horus and loses semen to him, Horus retaliates and impregnates Set, and Set comes into possession of Horus's eye, when it appears on Set's head. Because Thoth is a moon deity in addition to his other functions, it would make sense, according to te Velde, for Thoth to emerge in the form of the Eye and step in to mediate between the feuding deities. | Egyptologist Herman te Velde argues that the tradition about the lost testicles is a late variation on Set's loss of semen to Horus, and that the moon-like disk that emerges from Set's head after his impregnation is the Eye of Horus. If so, the episodes of mutilation and sexual abuse would form a single story, in which Set assaults Horus and loses semen to him, Horus retaliates and impregnates Set, and Set comes into possession of Horus's eye, when it appears on Set's head. Because Thoth is a [[moon]] deity in addition to his other functions, it would make sense, according to te Velde, for Thoth to emerge in the form of the Eye and step in to mediate between the feuding deities. | ||
The restoration of the eye of Horus to wholeness represents the return of the moon to full brightness, the return of the kingship to Horus, and many other aspects of ma'at. Sometimes the restoration of Horus's eye is accompanied by the restoration of Set's testicles, so that both gods are made whole near the conclusion of their feud. | The restoration of the eye of Horus to wholeness represents the return of the moon to full brightness, the return of the kingship to Horus, and many other aspects of ma'at. Sometimes the restoration of Horus's eye is accompanied by the restoration of Set's testicles, so that both gods are made whole near the conclusion of their feud. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
==Worship of Set== | ==Worship of Set== | ||
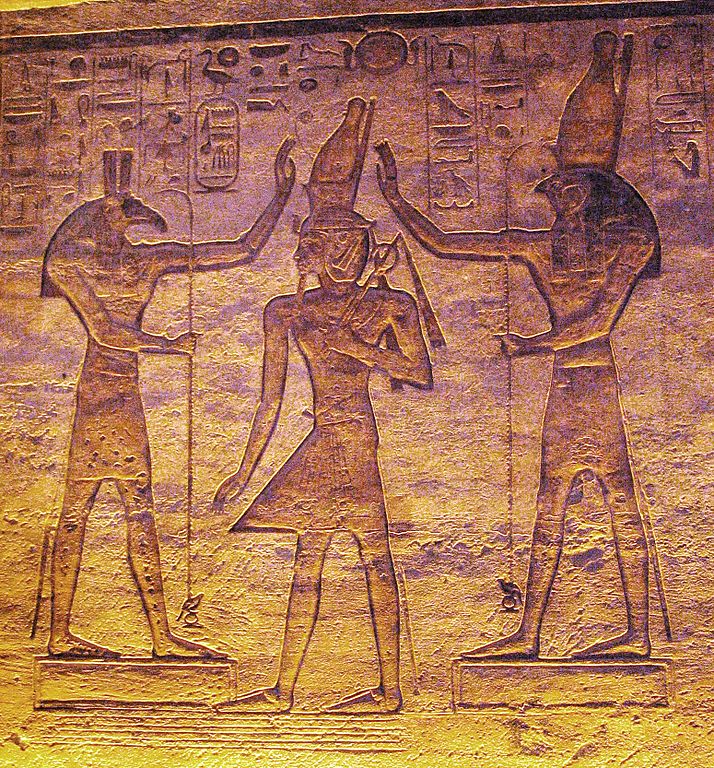
[[File:SethAndHorusAdoringRamsses.jpg|350px|thumb|The gods Seth (left) and Horus (right) adoring Ramesses in the small temple at Abu Simbel]] | [[File:SethAndHorusAdoringRamsses.jpg|350px|thumb|The gods Seth (left) and Horus (right) adoring Ramesses in the small temple at Abu Simbel]] | ||
The founder of the Nineteenth Dynasty, Ramesses I came from a military family from Avaris with strong ties to the priesthood of Set. Several of the Ramesside kings were named after the god, most notably Seti I (literally, "man of Set") and Setnakht (literally, "Set is strong"). In addition, one of the garrisons of Ramesses II held Set as its patron deity, and Ramesses II erected the so-called "Year 400 Stela" at Pi-Ramesses, commemorating the 400th anniversary of the Set cult in the Nile delta. | The founder of the Nineteenth Dynasty, Ramesses I came from a military family from Avaris with strong ties to the priesthood of Set. Several of the Ramesside kings were named after the god, most notably Seti I (literally, "man of Set") and Setnakht (literally, "Set is strong"). In addition, one of the garrisons of Ramesses II held Set as its patron deity, and Ramesses II erected the so-called "Year 400 Stela" at Pi-Ramesses, commemorating the 400th anniversary of the Set [[cult]] in the Nile delta. | ||
Set also became associated with foreign gods during the New Kingdom, particularly in the delta. Set was identified by the Egyptians with the Hittite deity Teshub, who, like Set, was a storm god, and the Canaanite deity [[Bael|Baal]], being worshipped together as "Seth-Baal." | Set also became associated with foreign gods during the New Kingdom, particularly in the delta. Set was identified by the Egyptians with the Hittite deity Teshub, who, like Set, was a storm god, and the Canaanite deity [[Bael|Baal]], being worshipped together as "Seth-Baal." | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
Set was worshipped at the temples of Ombos (Nubt near Naqada) and Ombos (Nubt near Kom Ombo), at Oxyrhynchus in Upper Egypt, and also in part of the Fayyum area. | Set was worshipped at the temples of Ombos (Nubt near Naqada) and Ombos (Nubt near Kom Ombo), at Oxyrhynchus in Upper Egypt, and also in part of the Fayyum area. | ||
More specifically, Set was worshipped in the relatively large metropolitan (yet provincial) locale of Sepermeru, especially during the Ramesside Period. There, Seth was honored with an important temple called the "House of Seth, Lord of Sepermeru." One of the epithets of this town was "gateway to the desert," which fits well with Set's role as a deity of the frontier regions of ancient Egypt. At Sepermeru, Set's temple enclosure included a small secondary shrine called "The House of Seth, Powerful-Is-His-Mighty-Arm," and Ramesses II himself built (or modified) a second land-owning temple for Nephthys, called "The House of Nephthys of Ramesses-Meriamun." | More specifically, Set was worshipped in the relatively large metropolitan (yet provincial) locale of Sepermeru, especially during the Ramesside Period. There, Seth was honored with an important temple called the "House of Seth, Lord of Sepermeru." One of the epithets of this town was "gateway to the desert," which fits well with Set's role as a deity of the frontier regions of ancient Egypt. At Sepermeru, Set's temple enclosure included a small secondary shrine called "The House of Seth, Powerful-Is-His-Mighty-Arm," and Ramesses II himself built (or modified) a second land-owning temple for Nephthys, called "The House of [[Nephthys]] of Ramesses-Meriamun." | ||
The two temples of Seth and Nephthys in Sepermeru were under separate administration, each with its own holdings and prophets. Moreover, another moderately sized temple of Seth is noted for the nearby town of Pi-Wayna. The close association of Seth temples with temples of Nephthys in key outskirt-towns of this milieu is also reflected in the likelihood that there existed another "House of Seth" and another "House of Nephthys" in the town of Su, at the entrance to the Fayyum. | The two temples of Seth and Nephthys in Sepermeru were under separate administration, each with its own holdings and prophets. Moreover, another moderately sized temple of Seth is noted for the nearby town of Pi-Wayna. The close association of Seth temples with temples of Nephthys in key outskirt-towns of this milieu is also reflected in the likelihood that there existed another "House of Seth" and another "House of Nephthys" in the town of Su, at the entrance to the Fayyum. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
[[Category:Egyptology]] | [[Category:Egyptology]] | ||
[[Category:Deities]] | [[Category:Deities]] | ||
[[Category:Egyptian gods]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:53, 15 November 2024
Set (/sɛt/; Egyptological: Sutekh - swtẖ ~ stẖ or Greek: Seth /sɛθ/) is a god of deserts, storms, disorder, violence, and foreigners in ancient Egyptian religion. In Ancient Greek, the god's name is given as Sēth (Σήθ). Set had a positive role where he accompanies Ra on his barque to repel Apep, the serpent of Chaos. Set had a vital role as a reconciled combatant. He was lord of the Red Land, where he was the balance to Horus' role as lord of the Black Land.
In the Osiris myth, Set is portrayed as the usurper who killed and mutilated his own brother, Osiris. Osiris's sister-wife, Isis, reassembled his corpse and resurrected her dead brother-husband with the help of the goddess Nephthys. The resurrection lasted long enough to conceive his son and heir, Horus. Horus sought revenge upon Set and many of the ancient Egyptian myths describe their conflicts.
Set was commonly associated with the planet Mercury. Since he is related to the west of Nile which is the Sahara, he is sometimes associated with a lesser deity, Ha, god of the desert, which is a deity depicted as a man with a desert determinative on his head.
Family
Set is the son of Geb, the Earth, and Nut, the Sky; his siblings are Osiris, Isis, and Nephthys. He married Nephthys and fathered Anubis and in some accounts, he had relationships with the foreign goddesses Anat and Astarte. From these relationships is said to be born a crocodile deity called Maga.
Name
The meaning of the name Set is unknown but it is thought to have been originally pronounced *sūtiẖ [ˈsuw.tixʲ] based on spellings of his name in Egyptian hieroglyphs as stẖ and swtẖ. The Late Egyptian spelling stš reflects the palatalization of ẖ while the eventual loss of the final consonant is recorded in spellings like swtj.
The Coptic form of the name, ⲥⲏⲧ Sēt, is the basis for the English vocalization.
Forms of Set
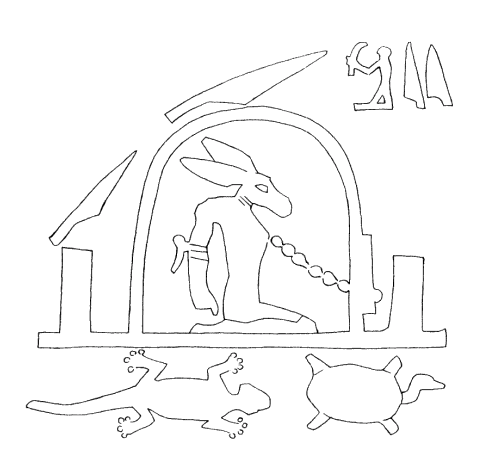
Set animal
Throughout the three thousand years of Egyptian civilization, Set took many forms according to various legends and stories about his activities. The most common of these was an enigmatic creature referred to by Egyptologists as the "Set animal," a beast not identified with any known animal, although it could be seen as a resembling an aardvark, an African wild dog, a donkey, a hyena, a jackal, a pig, an antelope, a giraffe, an okapi, a saluki, or a fennec fox. The animal has a downward curving snout; long ears with squared-off ends; a thin, forked tail with sprouted fur tufts in an inverted arrow shape; and a slender canine body. Sometimes, Set is depicted as a human with the distinctive head. Some early Egyptologists proposed that it was a stylised representation of the giraffe, owing to the large flat-topped "horns" which correspond to a giraffe's ossicones. The Egyptians themselves, however used distinct depictions for the giraffe and the Set animal. During the Late Period, Set was depicted as a donkey or as a man wearing a donkey's-head mask.
The earliest representations of what might be the Set animal comes from a tomb dating to the Amratian culture ("Naqada I") of prehistoric Egypt (3790–3500 BCE), though this identification is uncertain. If these are ruled out, then the earliest Set animal appears on a ceremonial macehead of King Scorpion II, a ruler of the Naqada III phase. The head and the forked tail of the Set animal are clearly present on the mace.
Black pig
The Dendera B zodiac ceiling depicts the Aryt decan as a male pig. This is derived from a story in the Coffin Texts involving Horus and Set. After Horus' eye is injured, Ra tells him to cover the eye and look at a black pig. Doing so causes Horus' good eye to also become injured because Set had transformed himself into a pig and projected the wound. For this reason, Ra declared that pigs are detestable and all his followers should consider the animal an abomination.
Egyptologist Bernard Arquier believes this is a reference to the New Moon, when the sky would have been darkest and Horus was absent.
Red ox / red goat
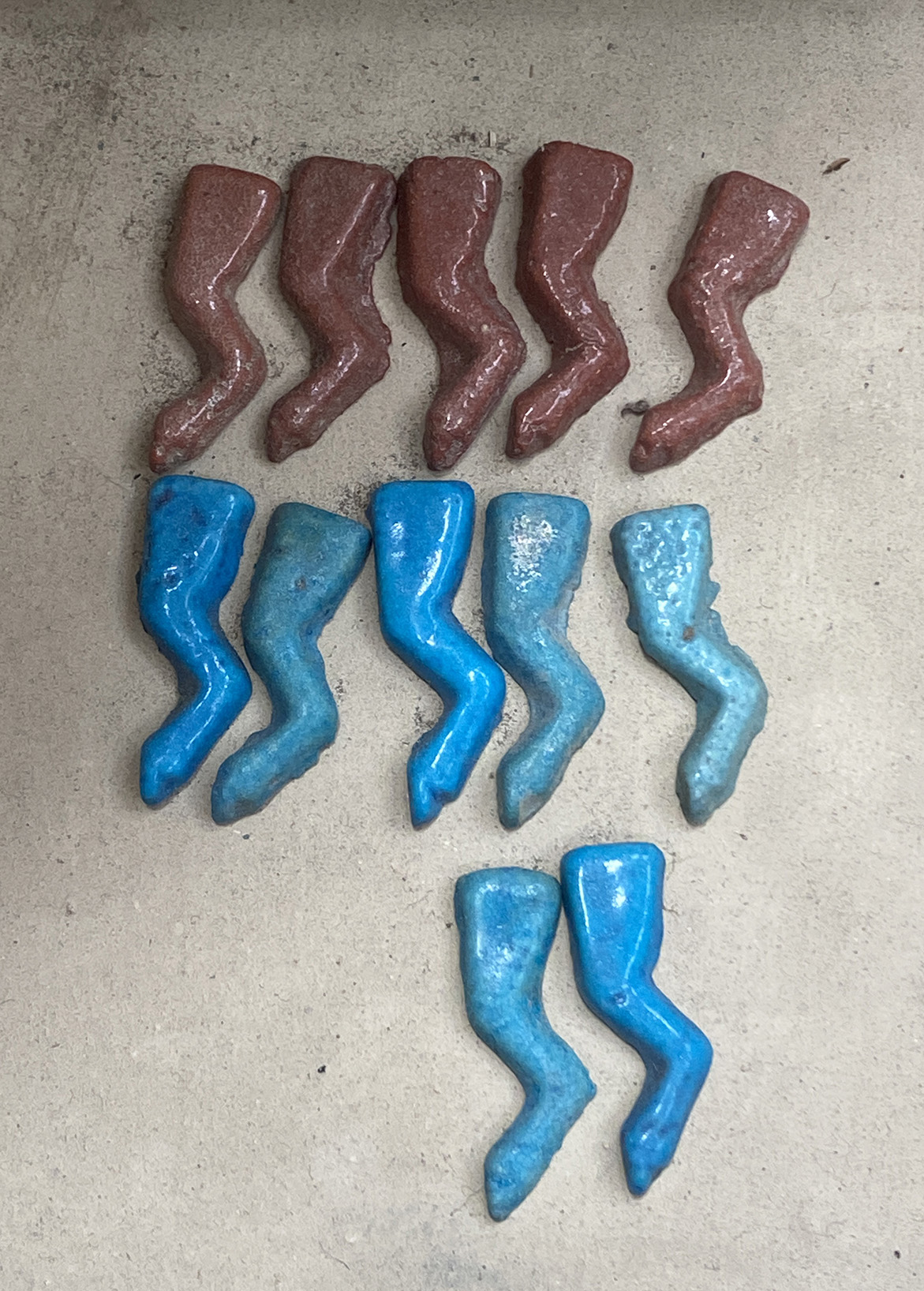
In a legend in the Pyramid Texts, as punishment for his rebellion and overthrow of Osiris, Set was transformed into a sacrificial red ox (some legends say a red goat). His foreleg (xpS) was cut off and thrown into the sky where it became Meskhetiu (Msxtyw), a group of seven stars in the northern sky (likely either Ursa Major or Ursa Minor).
The foreleg was not only a protective god, but it was also a lasting symbol of power and strength, especially of strength in the afterlife. Thousands of blue or red foreleg amulets have been found wrapped in the bandages of mummies across all periods of Egyptian history, and drawings of Msxtyw feature prominently alongside the decanal stars in the Middle Kingdom Period coffins.
During the Old Kingdom Period, it was common for the Pharaoh to wrestle a red ox in public to display his physical prowess and fitness to rule over the land. The foreleg of the defeated ox was severed and consumed as a symbol of his continued strength.
Conflict of Horus and Set
An important element of Set's mythology was his conflict with his brother/nephew, Horus, for the throne of Egypt. The contest between them is often violent but is also described as a legal judgment before the Ennead, an assembled group of Egyptian deities, to decide who should inherit the kingship. The judge in this trial may be Geb, who, as the father of Osiris and Set, held the throne before they did, or it may be the creator gods Ra or Atum, the originators of kingship. Other deities also take important roles: Thoth frequently acts as a conciliator in the dispute or as an assistant to the divine judge, and in "Contendings," Isis uses her cunning and magical power to aid her son.
The rivalry of Horus and Set is portrayed in two contrasting ways. Both perspectives appear as early as the Pyramid Texts, the earliest source of the myth. In some spells from these texts, Horus is the son of Osiris and nephew of Set, and the murder of Osiris is the major impetus for the conflict. The other tradition depicts Horus and Set as brothers. This incongruity persists in many of the subsequent sources, where the two gods may be called brothers or uncle and nephew at different points in the same text.
The divine struggle involves many episodes. "Contendings" describes the two gods appealing to various other deities to arbitrate the dispute and competing in different types of contests, such as racing in boats or fighting each other in the form of hippopotami, to determine a victor. In this account, Horus repeatedly defeats Set and is supported by most of the other deities. Yet the dispute drags on for eighty years, largely because the judge, the creator god, favors Set. In late ritual texts, the conflict is characterized as a great battle involving the two deities' assembled followers. The strife in the divine realm extends beyond the two combatants. At one point Isis attempts to harpoon Set as he is locked in combat with her son, but she strikes Horus instead, who then cuts off her head in a fit of rage. Thoth replaces Isis's head with that of a cow; the story gives a mythical origin for the cow-horn headdress that Isis commonly wears.
In a key episode in the conflict, Set rapes Horus. Set's violation is partly meant to degrade his rival, but it also involves homosexual desire, in keeping with one of Set's major characteristics, his forceful, potent, and indiscriminate sexuality. In the earliest account of this episode, in a fragmentary Middle Kingdom papyrus, the sexual encounter begins when Set asks to have sex with Horus, who agrees on the condition that Set will give Horus some of his strength. The encounter puts Horus in danger, because in Egyptian tradition semen is a potent and dangerous substance, akin to poison. According to some texts, Set's semen enters Horus's body and makes him ill, but in "Contendings", Horus thwarts Set by catching Set's semen in his hands. Isis retaliates by putting Horus's semen on lettuce-leaves that Set eats. Set's defeat becomes apparent when this semen appears on his forehead as a golden disk. He has been impregnated with his rival's seed and as a result "gives birth" to the disk. In "Contendings," Thoth takes the disk and places it on his own head; in earlier accounts, it is Thoth who is produced by this anomalous birth.
Another important episode concerns mutilations that the combatants inflict upon each other: Horus injures or steals Set's testicles and Set damages or tears out one, or occasionally both, of Horus's eyes. Sometimes the eye is torn into pieces. Set's mutilation signifies a loss of virility and strength. The removal of Horus's eye is even more important, for this stolen eye of Horus represents a wide variety of concepts in Egyptian religion. One of Horus's major roles is as a sky deity, and for this reason his right eye was said to be the sun and his left eye the moon. The theft or destruction of the eye of Horus is therefore equated with the darkening of the moon in the course of its cycle of phases, or during eclipses. Horus may take back his lost Eye, or other deities, including Isis, Thoth, and Hathor, may retrieve or heal it for him.
Egyptologist Herman te Velde argues that the tradition about the lost testicles is a late variation on Set's loss of semen to Horus, and that the moon-like disk that emerges from Set's head after his impregnation is the Eye of Horus. If so, the episodes of mutilation and sexual abuse would form a single story, in which Set assaults Horus and loses semen to him, Horus retaliates and impregnates Set, and Set comes into possession of Horus's eye, when it appears on Set's head. Because Thoth is a moon deity in addition to his other functions, it would make sense, according to te Velde, for Thoth to emerge in the form of the Eye and step in to mediate between the feuding deities.
The restoration of the eye of Horus to wholeness represents the return of the moon to full brightness, the return of the kingship to Horus, and many other aspects of ma'at. Sometimes the restoration of Horus's eye is accompanied by the restoration of Set's testicles, so that both gods are made whole near the conclusion of their feud.
Protector of Ra
Set was sometimes depicted standing on the prow of Ra's barge defeating the dark serpent Apep, the snake of chaos. In some Late Period representations, such as in the Persian Period Temple of Hibis at Khargah, Set was represented in this role with a falcon's head, taking on the guise of Horus. In the Amduat, Set is described as having a key role in overcoming Apep.
As protector of Ra, Set's birthday was celebrated during the epagomenal days which marked the end of the Egyptian calendar. His birthday was the third day, set aside to commemorate “The lord of life who is in front of the barque of Rē.”
Worship of Set
The founder of the Nineteenth Dynasty, Ramesses I came from a military family from Avaris with strong ties to the priesthood of Set. Several of the Ramesside kings were named after the god, most notably Seti I (literally, "man of Set") and Setnakht (literally, "Set is strong"). In addition, one of the garrisons of Ramesses II held Set as its patron deity, and Ramesses II erected the so-called "Year 400 Stela" at Pi-Ramesses, commemorating the 400th anniversary of the Set cult in the Nile delta.
Set also became associated with foreign gods during the New Kingdom, particularly in the delta. Set was identified by the Egyptians with the Hittite deity Teshub, who, like Set, was a storm god, and the Canaanite deity Baal, being worshipped together as "Seth-Baal."
Additionally, Set is depicted in part of the Greek Magical Papyri, a body of texts forming a grimoire used in Greco-Roman magic during the fourth century CE.
Temples of Set
Set was worshipped at the temples of Ombos (Nubt near Naqada) and Ombos (Nubt near Kom Ombo), at Oxyrhynchus in Upper Egypt, and also in part of the Fayyum area.
More specifically, Set was worshipped in the relatively large metropolitan (yet provincial) locale of Sepermeru, especially during the Ramesside Period. There, Seth was honored with an important temple called the "House of Seth, Lord of Sepermeru." One of the epithets of this town was "gateway to the desert," which fits well with Set's role as a deity of the frontier regions of ancient Egypt. At Sepermeru, Set's temple enclosure included a small secondary shrine called "The House of Seth, Powerful-Is-His-Mighty-Arm," and Ramesses II himself built (or modified) a second land-owning temple for Nephthys, called "The House of Nephthys of Ramesses-Meriamun."
The two temples of Seth and Nephthys in Sepermeru were under separate administration, each with its own holdings and prophets. Moreover, another moderately sized temple of Seth is noted for the nearby town of Pi-Wayna. The close association of Seth temples with temples of Nephthys in key outskirt-towns of this milieu is also reflected in the likelihood that there existed another "House of Seth" and another "House of Nephthys" in the town of Su, at the entrance to the Fayyum.
Seth's cult persisted even into the latter days of ancient Egyptian religion, in outlying but important places like Kharga, Dakhlah, Deir el-Hagar, Mut, and Kellis. In these places, Seth was considered "Lord of the Oasis / Town" and Nephthys was likewise venerated as "Mistress of the Oasis" at Seth's side, in his temples (esp. the dedication of a Nephthys-cult statue). Meanwhile, Nephthys was also venerated as "Mistress" in the Osirian temples of these districts as part of the specifically Osirian college. It would appear that the ancient Egyptians in these locales had little problem with the paradoxical dualities inherent in venerating Seth and Nephthys, as juxtaposed against Osiris, Isis, and Nephthys.