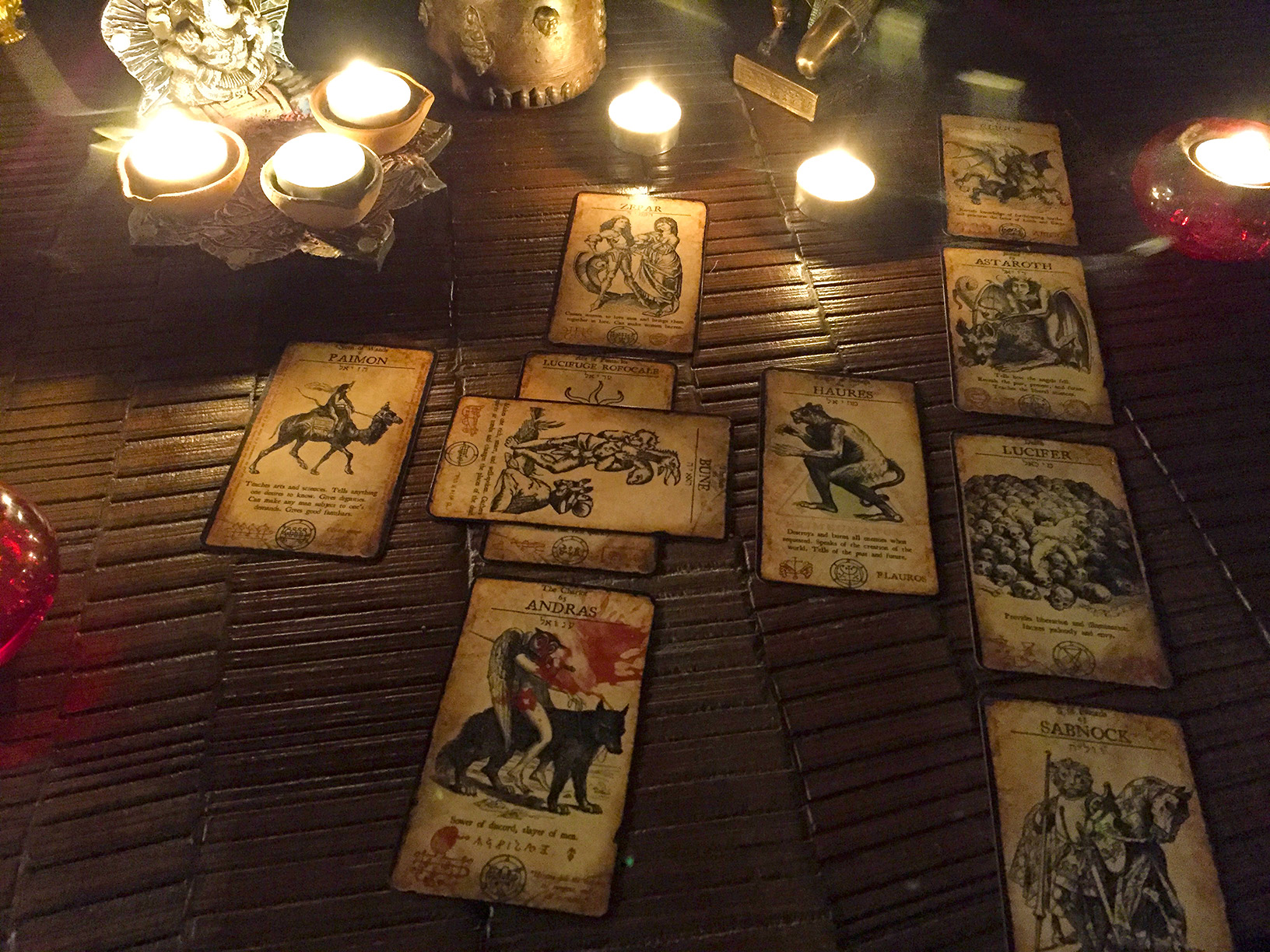
Divination
Divination (from Latin divinare, 'to foresee, to foretell, to predict, to prophesy') is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic, standardized process or ritual. Used in various forms throughout history, diviners ascertain their interpretations of how a querent should proceed by reading signs, events, or omens, or through alleged contact with a supernatural agency.
Divination can be seen as a systematic method with which to organize what appear to be disjointed, random facets of existence such that they provide insight into a problem at hand. If a distinction is to be made between divination and fortune-telling, divination has a more formal or ritualistic element and often contains a more social character, usually in a religious context, as seen in traditional African medicine. Fortune-telling, on the other hand, is a more everyday practice for personal purposes.
Particular divination methods vary by culture and religion.
Forms of divination
Many forms of divination have been used throughout history, with the oldest relying on signs from the natural world, such as earth, air, fire, and water. As civilization and technology progressed, new types of divination were discovered and implemented. Many of these persist in the present day. Some of the oldest forms of divination are:
- Aeromancy (air, wind, or clouds)
- Geomancy (earth or dirt)
- Hydromancy (water)
- Pyromancy (fire)
- Chiromancy (palmistry)
- Spatulamancy (bones of the scapula)
- Necromancy (spirits or body parts of the dead)
- Astrology (observing the stars)
- Scrying (reflective surfaces)
Origins
The history of divination varies widely across cultures and time periods, with many regional variations and significant differences, to the point where it is easier to examine the origin or evolution of specific types of divination (i.e. Tarot, Astrology, Scrying) rather than the history of divination as a whole.
The oldest methods used by Homo sapiens to determine the future can likely never be conclusively known, as they would predate antiquity and the written word. However, by examining the oldest confirmed methods, it appears that geomancy (studying formations in soil), celestial events (such as a solar eclipse, lunar eclipse, or the appearance of a comet), and examining the entrails of sacrificial animals would be the earliest techniques.
Ancient Egypt
The Oracle of Amun at the Siwa Oasis was made famous when Alexander the Great visited it after conquering Egypt from Persia in 332 BC. The oracle was revered for its ability to give prophecies and adjudicate disputes between local parties. Oracles were often written on pieces of discarded pottery called ostracon or on slips of papyrus and given by the temple priest to the person asking a question.
Ancient Greece
Both oracles and seers in ancient Greece practiced divination. Oracles were the conduits for the gods on earth; their prophecies were understood to be the will of the gods verbatim. Because of the high demand for oracle consultations and the oracles’ limited work schedule, they were not the main source of divination for the ancient Greeks. That role fell to the seers (Greek: μάντεις).
Seers were not in direct contact with the gods; instead, they were interpreters of signs provided by the gods. Seers used many methods to explicate the will of the gods including extispicy, bird signs, etc. They were more numerous than the oracles and did not keep a limited schedule; thus, they were highly valued by all Greeks, not just those with the capacity to travel to Delphi or other such distant sites.
Early Christian Europe
The divination method of casting lots (Cleromancy) was used by the remaining eleven disciples of Jesus in Acts 1:23-26 to select a replacement for Judas Iscariot. Therefore, divination was arguably an accepted practice in the early church. However, divination became viewed as a pagan practice by Christian emperors during ancient Rome.
In 692 the Quinisext Council, also known as the "Council in Trullo" in the Eastern Orthodox Church, passed canons to eliminate pagan and divination practices. Fortune-telling and other forms of divination were widespread through the Middle Ages. In the constitution of 1572 and public regulations of 1661 of Kur-Saxony, capital punishment was used on those predicting the future. Laws forbidding divination practice continue to this day.
Early Islamic Divination
In Islam, astrology(‘ilm ahkam al-nujum), the most widespread divinatory science, is the study of how celestial entities could be applied to the daily lives of people on earth. It is important to emphasize the practical nature of divinatory sciences because people from all socioeconomic levels and pedigrees sought the advice of astrologers to make important decisions in their lives. Astronomy was made a distinct science by intellectuals who did not agree with the former, although distinction may not have been made in daily practice, where astrology was technically outlawed and only tolerated if it was employed in public.
Astrologers, trained as scientists and astronomers, were able to interpret the celestial forces that ruled the "sub-lunar" to predict a variety of information from lunar phases and drought to times of prayer and the foundation of cities. The courtly sanction and elite patronage of Muslim rulers benefited astrologers’ intellectual statues.
The “science of the sand” (‘ilm al-raml), otherwise translated as geomancy, is “based on the interpretation of figures traced on sand or other surface known as tetragrams.” It is a good example of Islamic divination at a popular level. The core principle that meaning derives from a unique occupied position is identical to the core principle of astrology.
Pre-Columbian Americas
Divination was a central component of ancient Mesoamerican religious life. Many Aztec gods, including central creator gods, were described as diviners and were closely associated with sorcery. Tezcatlipoca is the patron of sorcerers and practitioners of magic. His name means "smoking mirror," a reference to a device used for divinatory scrying. In the Mayan Popol Vuh, the creator gods Xmucane and Xpiacoc perform divinatory hand casting during the creation of people. The Aztec Codex Borbonicus shows the original human couple, Oxomoco and Cipactonal, engaged in divining with kernels of maize. This primordial pair is associated with the ritual calendar, and the Aztecs considered them to be the first diviners.
Every civilization that developed in pre-Columbian Mexico, from the Olmecs to the Aztecs, practiced divination in daily life, both public and private. Scrying through the use of reflective water surfaces, mirrors, or the casting of lots were among the most widespread forms of divinatory practice. Visions derived from hallucinogens were another important form of divination, and are still widely used among contemporary diviners of Mexico. Among the more common hallucinogenic plants used in divination are morning glory, jimson weed, and peyote.
India and Nepal
Theyyam or "theiyam" in Malayalam - a south Indian language - is the process by which a devotee invites a Hindu god or goddess to use his or her body as a medium or channel and answer other devotees' questions. The same is called "arulvaakku" or "arulvaak" in Tamil, another south Indian language - Adhiparasakthi Siddhar Peetam is famous for arulvakku in Tamil Nadu. The people in and around Mangalore in Karnataka call the same, Buta Kola, "paathri" or "darshin"; in other parts of Karnataka, it is known by various names such as, "prashnaavali", "vaagdaana", "asei", "aashirvachana" and so on. In Nepal it is known as, "Devta ka dhaamee" or "jhaakri."
In English, the closest translation for these is, "oracle." The Dalai Lama, who lives in exile in northern India, still consults an oracle known as the Nechung Oracle, which is considered the official state oracle of the government of Tibet. The Dalai Lama has according to centuries-old custom, consulted the Nechung Oracle during the new year festivities of Losar.
Japan
Although Japan retains a history of traditional and local methods of divination, such as onmyōdō, contemporary divination in Japan, called uranai, derives from outside sources. Contemporary methods of divination in Japan include both Western and Chinese astrology, geomancy or feng shui, tarot cards, I Ching (Book of Changes) divination, and physiognomy (methods of reading the body to identify traits).
In Japan, divination methods include Futomani from the Shinto tradition.
Criticism
Divination has long been criticized. In the modern era, it has been dismissed by the scientific community and skeptics as being superstition; experiments do not support the idea that divination techniques can actually predict the future more reliably or precisely than would be possible without it. In antiquity, it was attacked by philosophers such as the Academic skeptic Cicero in De Divinatione and the Pyrrhonist Sextus Empiricus in Against the Astrologers. The satirist, Lucian, devoted a witty essay to Alexander the false prophet.