Difference between revisions of "King Solomon"
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) |
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
===Seal of Solomon=== | ===Seal of Solomon=== | ||
[[File:Seal of Solomon.png|250px|thumb|The Seal of Solomon]] | [[File:Seal of Solomon.png|250px|thumb|The Seal of Solomon]] | ||
A magic ring called the "[[Seal of Solomon]]" was given to Solomon and gave him power over demons or Jinn. The [[sigil|magical symbol]] said to have been on the Seal of Solomon which made it efficacious is often considered to be the Star of David though this emblem (also known as the Shield of David) is known to have been associated with Judaism only as recently as the 11th century CE while the five pointed star (pentagram) can be found on jars and other artifacts from Jerusalem dating back to at least the 2nd and 4th centuries BCE and is more likely to have been the emblem found on the ring purportedly used by King Solomon to control the Jinn or | A magic ring called the "[[Seal of Solomon]]" was given to Solomon and gave him power over demons or Jinn. The [[sigil|magical symbol]] said to have been on the Seal of Solomon which made it efficacious is often considered to be the Star of David though this emblem (also known as the Shield of David) is known to have been associated with Judaism only as recently as the 11th century CE while the five pointed star ([[pentagram]]) can be found on jars and other artifacts from Jerusalem dating back to at least the 2nd and 4th centuries BCE and is more likely to have been the emblem found on the ring purportedly used by King Solomon to control the Jinn or [[demon]]s. | ||
[[Asmoday|Asmodeus]], king of demons, was one day, according to the classical Rabbis, captured by Benaiah using the ring, and was forced to remain in Solomon's service. In one tale, Asmodeus brought a man with two heads from under the earth to show Solomon; the man, unable to return, married a woman from Jerusalem and had seven sons, six of whom resembled the mother, while one resembled the father in having two heads. After their father's death, the son with two heads claimed two shares of the inheritance, arguing that he was two men; Solomon decided that the son with two heads was only one man. | [[Asmoday|Asmodeus]], king of demons, was one day, according to the classical Rabbis, captured by Benaiah using the ring, and was forced to remain in Solomon's service. In one tale, Asmodeus brought a man with two heads from under the earth to show Solomon; the man, unable to return, married a woman from Jerusalem and had seven sons, six of whom resembled the mother, while one resembled the father in having two heads. After their father's death, the son with two heads claimed two shares of the inheritance, arguing that he was two men; Solomon decided that the son with two heads was only one man. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
===Solomon and Asmodeus=== | ===Solomon and Asmodeus=== | ||
[[File:HQ-Seal-of-Solomon.jpg|300px|thumb|The [[Secret Seal of Solomon]], which gave him power over the [[Goetic demon]]s.]] | [[File:HQ-Seal-of-Solomon.jpg|300px|thumb|The [[Secret Seal of Solomon]], which gave him power over the [[Goetic demon]]s.]] | ||
One legend concerning [[Asmoday|Asmodeus]] goes on to state that Solomon one day asked Asmodeus what could make demons powerful over man, and Asmodeus asked to be freed and given the ring so that he could demonstrate; Solomon agreed but Asmodeus threw the ring into the sea and it was swallowed by a fish. Asmodeus then swallowed the king, stood up fully with one wing touching heaven and the other earth, and spat out Solomon to a distance of 400 miles. The Rabbis claim this was a divine punishment for Solomon's having failed to follow three divine commands, and Solomon was forced to wander from city to city, until he eventually arrived in an Ammonite city where he was forced to work in the king's kitchens. | One legend concerning [[Asmoday|Asmodeus]] goes on to state that Solomon one day asked Asmodeus what could make demons powerful over man, and Asmodeus asked to be freed and given the ring so that he could demonstrate; Solomon agreed but Asmodeus threw the ring into the sea and it was swallowed by a fish. Asmodeus then swallowed the king, stood up fully with one wing touching [[heaven]] and the other [[earth]], and spat out Solomon to a distance of 400 miles. The Rabbis claim this was a divine punishment for Solomon's having failed to follow three divine commands, and Solomon was forced to wander from city to city, until he eventually arrived in an Ammonite city where he was forced to work in the king's kitchens. | ||
Solomon gained a chance to prepare a meal for the Ammonite king, which the king found so impressive that the previous cook was sacked and Solomon put in his place; the king's daughter, Naamah, subsequently fell in love with Solomon, but the family (thinking Solomon a commoner) disapproved, so the king decided to kill them both by sending them into the desert. Solomon and the king's daughter wandered the desert until they reached a coastal city, where they bought a fish to eat, which just happened to be the one which had swallowed the magic ring. Solomon was then able to regain his throne and expel Asmodeus. The element of a ring thrown into the sea and found back in a fish's belly also appeared in Herodotus' account of Polycrates, the tyrant of Samos (c. 538–522 BCE). | Solomon gained a chance to prepare a meal for the Ammonite king, which the king found so impressive that the previous cook was sacked and Solomon put in his place; the king's daughter, Naamah, subsequently fell in love with Solomon, but the family (thinking Solomon a commoner) disapproved, so the king decided to kill them both by sending them into the desert. Solomon and the king's daughter wandered the desert until they reached a coastal city, where they bought a fish to eat, which just happened to be the one which had swallowed the magic ring. Solomon was then able to regain his throne and expel Asmodeus. The element of a ring thrown into the sea and found back in a fish's belly also appeared in Herodotus' account of Polycrates, the tyrant of Samos (c. 538–522 BCE). | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
[[Category:People]] | [[Category:People]] | ||
[[Category:Occultists]] | [[Category:Occultists]] | ||
[[Category:Monarchs]] | [[Category:Monarchs]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:42, 19 November 2024
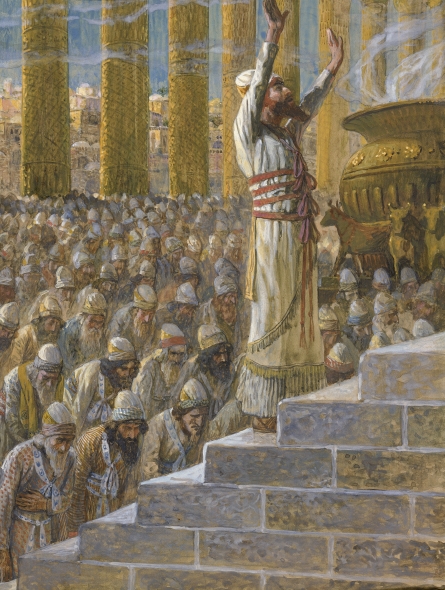
King Solomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew: יְדִידְיָהּ Yəḏīḏəyāh), was, according to the Hebrew Bible or Old Testament, a fabulously wealthy and wise king of the United Kingdom of Israel who succeeded his father, David. The conventional dates of Solomon's reign are about 970–931 BCE, normally given in alignment with the dates of David's reign. He is described as king of the United Monarchy, which broke apart into the northern Kingdom of Israel and the southern Kingdom of Judah shortly after his death. Following the split, his patrilineal descendants ruled over Judah alone.
In Abrahamic religions
According to the Talmud, Solomon is one of the 48 Jewish prophets. In the Quran, he is considered to be a major Islamic prophet, and Muslims generally refer to him as Sulaiman ibn Dawud (Arabic: سُلَيْمَان بْن دَاوُوْد, lit. 'Solomon, son of David').
The Hebrew Bible identifies Solomon as the builder of the First Temple in Jerusalem, beginning in the fourth year of his reign using the vast wealth he and his father had accumulated; he dedicated the temple to Yahweh, the God of Israel. Solomon is portrayed as great in wisdom, wealth and power beyond either of the previous kings of the country.
Apocryphal texts
He is the subject of many other later references and legends, most notably in the 1st-century apocryphal work known as the Testament of Solomon. In the New Testament, he is portrayed as a teacher of wisdom excelled by Jesus Christ, and as arrayed in glory, but excelled by "the lilies of the field."
Rabbinical tradition attributes the Wisdom of Solomon (included within the Septuagint) to Solomon, although this book was probably written in the 2nd century BCE. In this work, Solomon is portrayed as an astronomer. Other books of wisdom poetry such as the Odes of Solomon and the Psalms of Solomon also bear his name. The Jewish historian Eupolemus, who wrote about 157 BCE, included copies of apocryphal letters exchanged between Solomon and the kings of Egypt and Tyre.
The Gnostic Apocalypse of Adam, which may date to the 1st or 2nd century, refers to a legend in which Solomon sends out an army of demons to seek a virgin who had fled from him, perhaps the earliest surviving mention of the later common tale that Solomon controlled demons and made them his slaves. This tradition of Solomon's control over demons appears fully elaborated in the early pseudographical work called the Testament of Solomon with its elaborate and grotesque demonology.
As a magician
In later years, in mostly non-biblical circles, Solomon also came to be known as a magician and an exorcist, with numerous amulets and medallion seals dating from the Hellenistic period invoking his name.
Angels and magic
According to the Rabbinical literature, on account of his modest request for wisdom only, Solomon was rewarded with riches and an unprecedented glorious realm, which extended over the upper world inhabited by the angels and over the whole of the terrestrial globe with all its inhabitants, including all the beasts, fowl, and reptiles, as well as the demons and spirits. His control over the demons, spirits, and animals augmented his splendor, the demons bringing him precious stones, besides water from distant countries to irrigate his exotic plants. The beasts and fowl of their own accord entered the kitchen of Solomon's palace, so that they might be used as food for him, and extravagant meals for him were prepared daily by each of his 700 wives and 300 concubines, with the thought that perhaps the king would feast that day in her house.
According to the Lesser Key of Solomon, King Solomon is responsible for conjuring the 72 Goetic demons.
Seal of Solomon
A magic ring called the "Seal of Solomon" was given to Solomon and gave him power over demons or Jinn. The magical symbol said to have been on the Seal of Solomon which made it efficacious is often considered to be the Star of David though this emblem (also known as the Shield of David) is known to have been associated with Judaism only as recently as the 11th century CE while the five pointed star (pentagram) can be found on jars and other artifacts from Jerusalem dating back to at least the 2nd and 4th centuries BCE and is more likely to have been the emblem found on the ring purportedly used by King Solomon to control the Jinn or demons.
Asmodeus, king of demons, was one day, according to the classical Rabbis, captured by Benaiah using the ring, and was forced to remain in Solomon's service. In one tale, Asmodeus brought a man with two heads from under the earth to show Solomon; the man, unable to return, married a woman from Jerusalem and had seven sons, six of whom resembled the mother, while one resembled the father in having two heads. After their father's death, the son with two heads claimed two shares of the inheritance, arguing that he was two men; Solomon decided that the son with two heads was only one man.
The Seal of Solomon, in some legends known as the Ring of Aandaleeb, was a highly sought after symbol of power. In several legends, different groups or individuals attempted to steal it or attain it in some manner. A similar symbol known as the Secret Seal of Solomon is also used to constrain the power of demons.
Solomon and Asmodeus
One legend concerning Asmodeus goes on to state that Solomon one day asked Asmodeus what could make demons powerful over man, and Asmodeus asked to be freed and given the ring so that he could demonstrate; Solomon agreed but Asmodeus threw the ring into the sea and it was swallowed by a fish. Asmodeus then swallowed the king, stood up fully with one wing touching heaven and the other earth, and spat out Solomon to a distance of 400 miles. The Rabbis claim this was a divine punishment for Solomon's having failed to follow three divine commands, and Solomon was forced to wander from city to city, until he eventually arrived in an Ammonite city where he was forced to work in the king's kitchens.
Solomon gained a chance to prepare a meal for the Ammonite king, which the king found so impressive that the previous cook was sacked and Solomon put in his place; the king's daughter, Naamah, subsequently fell in love with Solomon, but the family (thinking Solomon a commoner) disapproved, so the king decided to kill them both by sending them into the desert. Solomon and the king's daughter wandered the desert until they reached a coastal city, where they bought a fish to eat, which just happened to be the one which had swallowed the magic ring. Solomon was then able to regain his throne and expel Asmodeus. The element of a ring thrown into the sea and found back in a fish's belly also appeared in Herodotus' account of Polycrates, the tyrant of Samos (c. 538–522 BCE).
In another familiar version of the legend of the Seal of Solomon, Asmodeus disguises himself. In some myths, he's disguised as King Solomon himself, while in more frequently heard versions he's disguised as a falcon, calling himself Gavyn (Gavinn or Gavin), one of King Solomon's trusted friends. The concealed Asmodeus tells travelers who have ventured up to King Solomon's grand lofty palace that the Seal of Solomon was thrown into the sea. He then convinces them to plunge in and attempt to retrieve it, for if they do they would take the throne as king.