Difference between revisions of "Kabbalah"
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) |
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Mystical revelation== | ==Mystical revelation== | ||
When read by later generations of Kabbalists, the Torah's description of the creation in the Book of Genesis reveals mysteries about [[Yahweh|God]] himself. The [[Bible]] provides ample additional material for mythic and mystical speculation. The prophet Ezekiel's visions in particular attracted much mystical speculation, as did Isaiah's Temple vision. Other mystical events include Jacob's vision of the ladder to heaven, and Moses' encounters with the Burning bush and God on Mount Sinai. | When read by later generations of Kabbalists, the Torah's description of the creation in the Book of Genesis reveals mysteries about [[Yahweh|God]] himself. The [[Bible]] provides ample additional material for mythic and mystical speculation. The [[prophet]] Ezekiel's visions in particular attracted much mystical speculation, as did Isaiah's Temple vision. Other mystical events include Jacob's vision of the ladder to heaven, and Moses' encounters with the Burning bush and God on Mount Sinai. | ||
The [[Shem HaMephorash|72 letter name of God]] which is used in Jewish mysticism for meditation purposes is derived from the Hebrew verbal utterance Moses spoke in the presence of an angel, while the Sea of Reeds parted, allowing the Hebrews to escape their approaching attackers. This was subsequently incorporated into [[ritual magic]] in the names of the 72 [[Kabbalistic angel]]s. | The [[Shem HaMephorash|72 letter name of God]] which is used in Jewish mysticism for meditation purposes is derived from the Hebrew verbal utterance Moses spoke in the presence of an angel, while the Sea of Reeds parted, allowing the Hebrews to escape their approaching attackers. This was subsequently incorporated into [[ritual magic]] in the names of the 72 [[Kabbalistic angel]]s. | ||
Revision as of 09:57, 15 March 2022
Kabbalah (from Hebrew קַבָּלָה (qabalah) 'reception, accounting') is a Western esoteric tradition involving mysticism and the occult. It is the underlying philosophy and framework for magical societies such as the Golden Dawn, Thelemic orders, mystical-religious societies such as the Builders of the Adytum and the Fellowship of the Rosy Cross, and is a precursor to the Neopagan, Wiccan and New Age movements.
The Kabbalah as used by ritual magicians differs from the Jewish form in being a more admittedly syncretic system, however it shares many concepts with Jewish Kabbalah.
Non-religious Kabbalistic practices are sometimes called "Hermetic Qabalah," despite having religious overtones.
History
Traditionalist Judaic views of Kabbalah's origins view it as an original development from within the Jewish religion, perhaps expressed through syncretic terminology from Medieval Jewish Neoplatonism. Contemporary academics of Jewish mysticism have reassessed Gershom Scholem's theory that the new doctrine of Medieval Kabbalah assimilated an earlier Jewish version of Gnosticism; Moshe Idel instead has posited a historical continuity of development from early Jewish mysticism.
In contrast, Hermeticists have taken different views of Qabalah's origins. Some authors see the origins of Qabalah not in Semitic/Jewish mysticism or ancient Egyptian Gnosticism, but in a western tradition originating in classical Greece with Indo-European cultural roots, later adopted by Jewish mystics. According to this view, "Hermetic Qabalah" would be the original Qabalah, even though the word itself is Judaic Hebrew, over the Christian Cabalah or the Jewish Kabbalah.
Renaissance magic
Jewish Kabbalah was absorbed into the Hermetic tradition at least as early as the 15th century when Giovanni Pico della Mirandola promoted a syncretic worldview combining Platonism, Neoplatonism, Aristotelianism, Hermeticism and Kabbalah. Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa, a German magician, occult writer, theologian, astrologer, and alchemist, wrote the influential Three Books of Occult Philosophy, incorporating Kabbalah in its theory and practice of Western magic. It contributed strongly to the Renaissance view of ritual magic's relationship with Christianity.
Pico's Hermetic syncretism was further developed by Athanasius Kircher, a Jesuit priest, hermeticist and polymath, who wrote extensively on the subject in 1652, bringing further elements such as Orphism and the Egyptian religion to the mix.
Concept of divinity
A primary concern of Kabbalah is the nature of divinity, its conception of which is quite markedly different from that presented in monotheistic religions; in particular there is not the strict separation between divinity and humankind which is seen in monotheisms. Kabbalah holds to the Neoplatonic conception that the manifest universe, of which material creation is a part, arose as a series of emanations from the godhead.
Mystical revelation
When read by later generations of Kabbalists, the Torah's description of the creation in the Book of Genesis reveals mysteries about God himself. The Bible provides ample additional material for mythic and mystical speculation. The prophet Ezekiel's visions in particular attracted much mystical speculation, as did Isaiah's Temple vision. Other mystical events include Jacob's vision of the ladder to heaven, and Moses' encounters with the Burning bush and God on Mount Sinai.
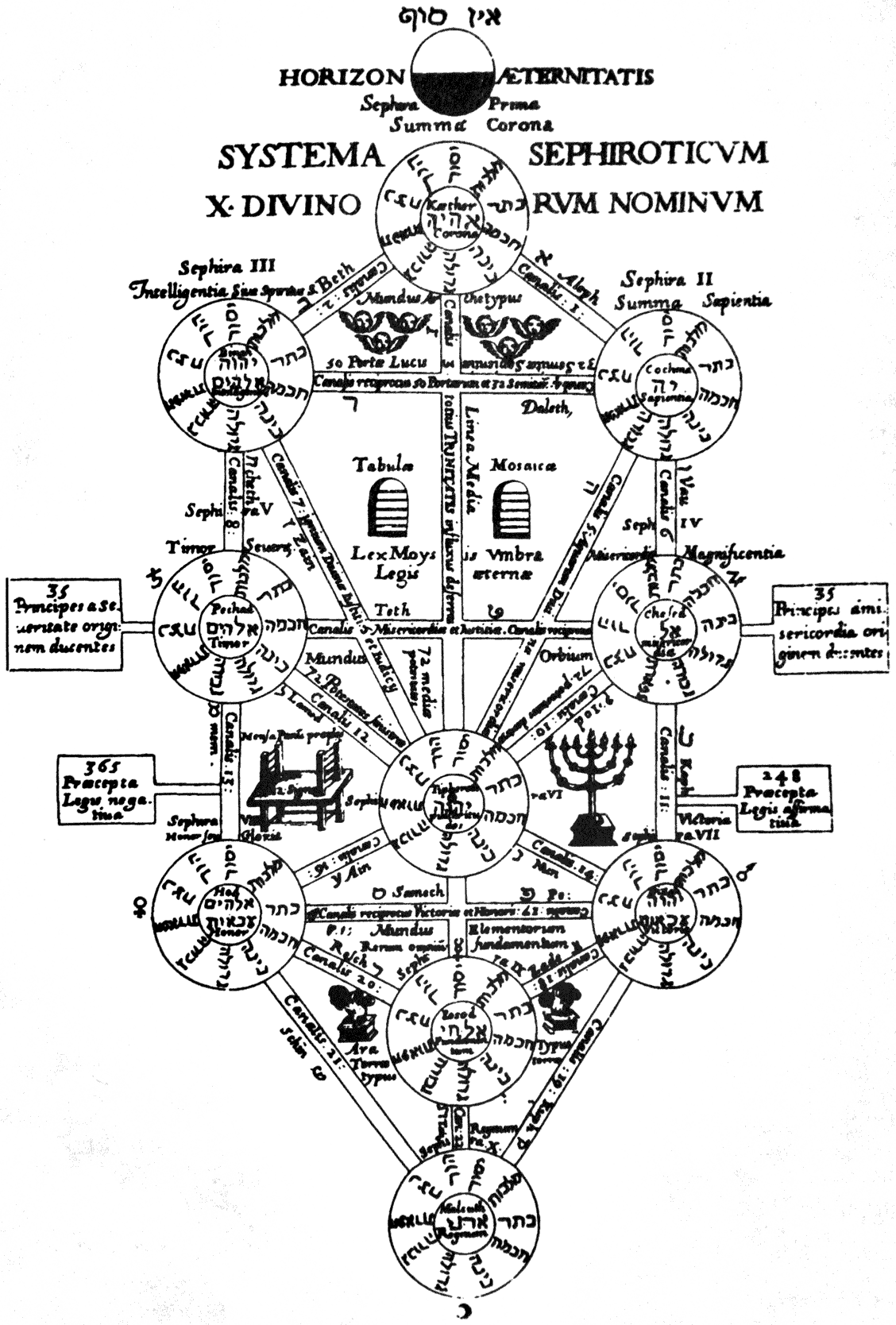
The 72 letter name of God which is used in Jewish mysticism for meditation purposes is derived from the Hebrew verbal utterance Moses spoke in the presence of an angel, while the Sea of Reeds parted, allowing the Hebrews to escape their approaching attackers. This was subsequently incorporated into ritual magic in the names of the 72 Kabbalistic angels.
Primary texts
Many texts have been produced, that are important to Kabbalistic doctrine, among them the ancient descriptions of Sefer Yetzirah, the Heichalot mystical ascent literature, the Bahir, Sefer Raziel HaMalakh and the Zohar, the main text of Kabbalistic exegesis.
Sefer ha-Razim, was, according to the Kabbalists, transmitted by the angel Raziel to Adam after he was evicted from Eden. Another famous work, the early Sefer Yetzirah, is dated back to the patriarch Abraham. This tendency toward pseudepigraphy has its roots in apocalyptic literature, which claims that esoteric knowledge such as magic, divination and astrology was transmitted to humans in the mythic past by the two angels, Aza and Azazel (in other places, Azaz'el and Uzaz'el) who fell from heaven.
As well as ascribing ancient origins to texts, and reception of Oral Torah transmission, the greatest and most innovative Kabbalists claimed mystical reception of direct personal divine revelations, by heavenly mentors such as Elijah the Prophet, the souls of Talmudic sages, prophetic revelation, soul ascents on high, etc. On this basis, Arthur Green speculates, that while the Zohar was written by a circle of Kabbalists in medieval Spain, they may have believed they were channeling the souls and direct revelations from the earlier mystic circle of Shimon bar Yochai in 2nd century Galilee depicted in the Zohar's narrative. Academics have compared the Zohar mystic circle of Spain with the romanticised wandering mystic circle of Galilee described in the text.