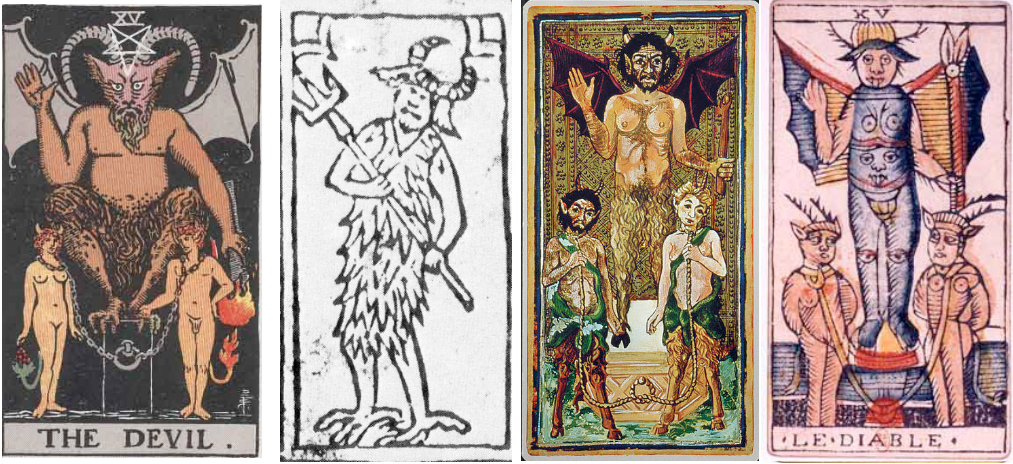
Difference between revisions of "Satan"
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) (Created page with "500px|thumb|Four Tarot cards showing depictions of The Devil from the [[Major Arcana.]] '''Satan''', also known as The Devil is an entity in the A...") |
Occultwiki (talk | contribs) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:The Devil.png|500px|thumb|Four Tarot cards showing depictions of The Devil from the [[Major Arcana]].]] | [[File:The Devil.png|500px|thumb|Four Tarot cards showing depictions of The Devil from the [[Major Arcana]].]] | ||
'''Satan''', also known as [[The Devil]] is an entity in the [[Abrahamic religion]]s that seduces humans into sin or falsehood. In [[Judaism]], Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the'' yetzer hara'', or "evil inclination." | '''Satan''', also known as [[The Devil]] is an entity in the [[Abrahamic religion]]s that seduces humans into sin or falsehood. In [[Judaism]], Satan is seen as an agent subservient to [[Yahweh|God]], typically regarded as a metaphor for the'' yetzer hara'', or "evil inclination." | ||
In [[Christianity]] and [[Islam]], he is usually seen as a [[fallen angel]] that has rebelled against God, who nevertheless allows him temporary power over the fallen world and a host of [[demon]]s. | |||
==Satan in Judaism== | ==Satan in Judaism== | ||
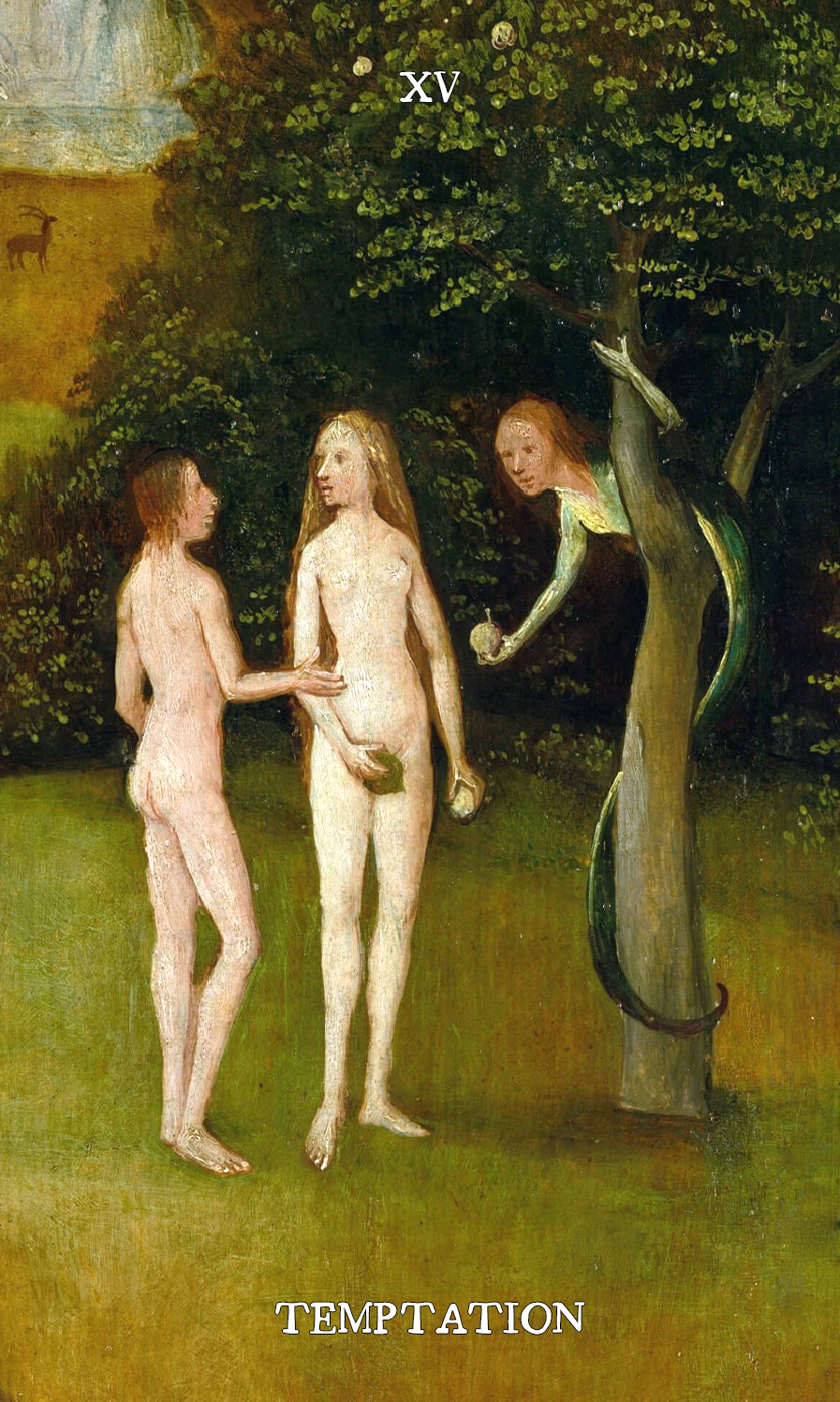
[[File:Temptation.jpg|300px|thumb|The Temptation card from [[The Hieronymus Bosch Tarot]] depicting the serpent in the Garden of Eden]] | [[File:Temptation.jpg|300px|thumb|The Temptation card from [[Hieronymus Bosch Tarot|The Hieronymus Bosch Tarot]] depicting the serpent in the [[Garden of Eden]]]] | ||
The original Hebrew term ''śāṭān'' (Hebrew: שָׂטָן) is a generic noun meaning "accuser" or "adversary", which is used throughout the [[ | The original Hebrew term ''śāṭān'' (Hebrew: שָׂטָן) is a generic noun meaning "accuser" or "adversary", which is used throughout the [[Bible]] to refer to ordinary human adversaries, as well as a specific supernatural entity. The word is derived from a verb meaning primarily "to obstruct, oppose". When it is used without the definite article (simply satan), the word can refer to any accuser, but when it is used with the definite article (ha-satan), it usually refers specifically to the [[heaven]]ly accuser: the satan. | ||
The word with the definite article Ha-Satan (Hebrew: הַשָּׂטָן) occurs 17 times in the Masoretic Text, in two books of the Hebrew Bible: Job ch. 1–2 (14×) and Zechariah 3:1–2 (3×). | The word with the definite article Ha-Satan (Hebrew: הַשָּׂטָן) occurs 17 times in the Masoretic Text, in two books of the Hebrew Bible: Job ch. 1–2 (14×) and Zechariah 3:1–2 (3×). A figure known as ha-satan ("the satan") first appears in the Tanakh as a heavenly prosecutor, a member of the sons of God subordinate to [[Yahweh]], who prosecutes the nation of Judah in the heavenly court and tests the loyalty of Yahweh's followers. During the intertestamental period, possibly due to influence from the Zoroastrian figure of Angra Mainyu, ha-satan developed into a malevolent entity with abhorrent qualities in dualistic opposition to God. In the apocryphal Book of Jubilees, Yahweh grants ha-satan (referred to as Mastema) authority over a group of fallen angels, or their offspring, to tempt humans to sin and punish them. | ||
The [[Second Book of Enoch]], also called the Slavonic Book of Enoch, contains references to a Watcher called | The [[Book of Enoch|Second Book of Enoch]], also called the Slavonic Book of Enoch, contains references to a Watcher called Satanael. It is a pseudepigraphic text of an uncertain date and unknown authorship. The text describes Satanael as being the prince of the Grigori who was cast out of heaven and an evil spirit who knew the difference between what was "righteous" and "sinful". In the Book of Wisdom, the devil is taken to be the being who brought death into the world, but originally the culprit was recognized as Cain. The name [[Samael]], which is used in reference to one of the fallen angels, later became a common name for Satan in Jewish Midrash and [[Kabbalah]]. | ||
===Modern beliefs=== | ===Modern beliefs=== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Satan in Christianity== | ==Satan in Christianity== | ||
[[File:Codex Gigas devil.jpg|300px|thumb|Illustration of the Devil in the ''Codex Gigas'']] | |||
The [[Book of Revelation]] represents Satan as the supernatural ruler of the Roman Empire and the ultimate cause of all evil in the world. In Revelation 2:9–10, as part of the letter to the church at Smyrna, John of Patmos refers to the Jews of Smyrna as "a synagogue of Satan" and warns that "the Devil is about to cast some of you into prison as a test, and for ten days you will have affliction." In Revelation 2:13–14, in the letter to the church of Pergamum, John warns that Satan lives among the members of the congregation and declares that "Satan's throne" is in their midst. Pergamum was the capital of the Roman Province of Asia and "Satan's throne" may be referring to the monumental Pergamon Altar in the city, which was dedicated to the Greek god Zeus, or to a temple dedicated to the Roman emperor Augustus. | The [[Book of Revelation]] represents Satan as the supernatural ruler of the Roman Empire and the ultimate cause of all evil in the world. In Revelation 2:9–10, as part of the letter to the church at Smyrna, John of Patmos refers to the Jews of Smyrna as "a synagogue of Satan" and warns that "the Devil is about to cast some of you into prison as a test, and for ten days you will have affliction." In Revelation 2:13–14, in the letter to the church of Pergamum, John warns that Satan lives among the members of the congregation and declares that "Satan's throne" is in their midst. Pergamum was the capital of the Roman Province of Asia and "Satan's throne" may be referring to the monumental Pergamon Altar in the city, which was dedicated to the Greek god Zeus, or to a temple dedicated to the Roman emperor Augustus. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
The primary characteristic of Satan, aside from his hubris and despair, is his ability to cast evil suggestions (waswās) into men and women. In the Quran, 15:45 states that Satan has no influence over the righteous, but that those who fall in error are under his power. 7:156 implies that those who obey God's laws are immune to the temptations of Satan. 56:79 warns that Satan tries to keep Muslims from reading the Quran and 16:98–100 recommends reciting the Quran as an antidote against Satan. 35:6 refers to Satan as the enemy of humanity and 36:60 forbids humans from worshipping him. In the Quranic retelling of the story of Job, Job knows that Satan is the one tormenting him. | The primary characteristic of Satan, aside from his hubris and despair, is his ability to cast evil suggestions (waswās) into men and women. In the Quran, 15:45 states that Satan has no influence over the righteous, but that those who fall in error are under his power. 7:156 implies that those who obey God's laws are immune to the temptations of Satan. 56:79 warns that Satan tries to keep Muslims from reading the Quran and 16:98–100 recommends reciting the Quran as an antidote against Satan. 35:6 refers to Satan as the enemy of humanity and 36:60 forbids humans from worshipping him. In the Quranic retelling of the story of Job, Job knows that Satan is the one tormenting him. | ||
During the first two centuries of Islam, Muslims almost unanimously accepted the traditional story known as the [[Satanic Verses]] as true. According to this narrative, Muhammad was told by Satan to add words to the Quran which would allow Muslims to pray for the intercession of pagan goddesses. He mistook the words of Satan for divine inspiration. Modern Muslims almost universally reject this story as heretical, as it calls the integrity of the Quran into question. | During the first two centuries of [[Islam]], Muslims almost unanimously accepted the traditional story known as the [[Satanic Verses]] as true. According to this narrative, Muhammad was told by Satan to add words to the Quran which would allow Muslims to pray for the intercession of [[pagan]] goddesses. He mistook the words of Satan for divine inspiration. Modern Muslims almost universally reject this story as heretical, as it calls the integrity of the Quran into question. | ||
On the third day of the Hajj, Muslim pilgrims to Mecca throw seven stones at a pillar known as the Jamrah al-’Aqabah, symbolizing the stoning of the Devil. This ritual is based on the Islamic tradition that, when God ordered Abraham to sacrifice his son Ishmael, Satan tempted him three times not to do it, and, each time, Abraham responded by throwing seven stones at him. | On the third day of the Hajj, Muslim pilgrims to Mecca throw seven stones at a pillar known as the Jamrah al-’Aqabah, symbolizing the stoning of the Devil. This ritual is based on the Islamic tradition that, when God ordered Abraham to sacrifice his son Ishmael, Satan tempted him three times not to do it, and, each time, Abraham responded by throwing seven stones at him. | ||
==Occult correspondences== | |||
In the [[hierarchy of Hell]], Satan is the [[demon]] prince of the Deluders, the 5th degree of diabolical spirits. In this context, he is connected [[astrology|astrologically]] with the planet [[Mars]]. | |||
In [[Kabbalah]], Satan (alongside [[Moloch]]) is the demon ruler over the [[qlippoth]] of [[Thaumiel]] on the [[Tree of Death]]. | |||
==Satanism== | ==Satanism== | ||
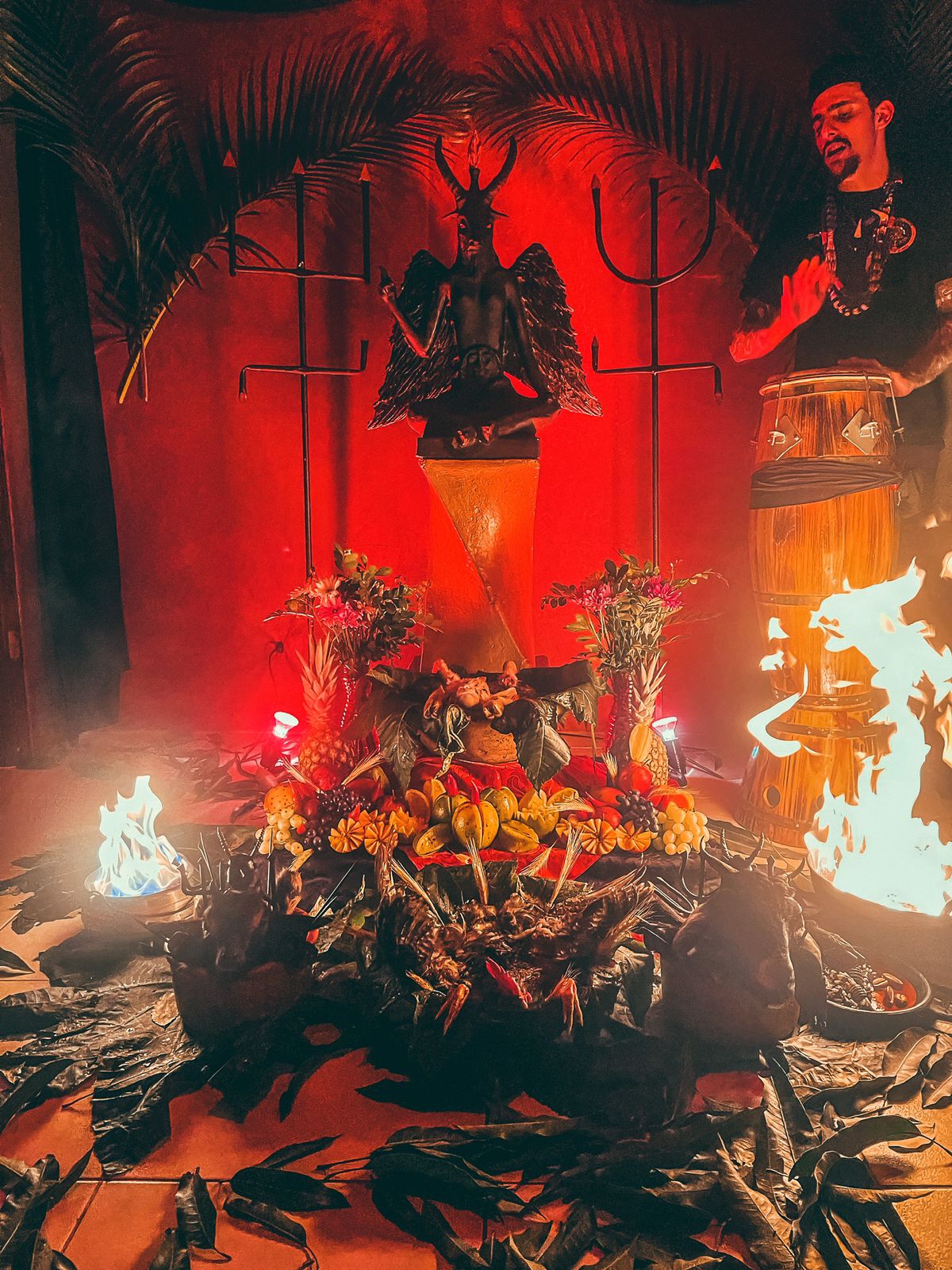
[[File: | [[File:Quimbanda Ritual.jpg|400px|thumb|A Quimbanda ritual featuring a statue of [[Baphomet]]]] | ||
===Theistic Satanism=== | ===Theistic Satanism=== | ||
Theistic Satanism, commonly referred to as "devil worship", views Satan as a deity, whom individuals may supplicate to. It consists of loosely affiliated or independent groups and cabals, which all agree that Satan is a real entity. | Theistic Satanism, commonly referred to as "devil worship", views Satan as a deity, whom individuals may supplicate to. It consists of loosely affiliated or independent groups and cabals, which all agree that Satan is a real entity. | ||
The [[African diaspora religion|Afro-Brazilian religion]] of [[Quimbanda]] regards itself as worshipping [[the Devil]] and other spirits called ''exús'' that, while not inherently evil, are similar to [[demon]]s. | |||
===Atheistic Satanism=== | ===Atheistic Satanism=== | ||
| Line 46: | Line 54: | ||
==Accusations of Satan Worship== | ==Accusations of Satan Worship== | ||
The main deity in the tentatively Indo-European pantheon of the [[Yazidis]], Melek Taus, is similar to the devil in Christian and Islamic traditions, as he refused to bow down before humanity. Therefore, Christians and Muslims often consider Melek Taus to be Satan. However, rather than being Satanic, Yazidism can be understood as a remnant of a pre-Islamic Middle Eastern Indo-European religion, and/or a ghulat | The main deity in the tentatively Indo-European pantheon of the [[Yazidism|Yazidis]], Melek Taus, is similar to the devil in Christian and Islamic traditions, as he refused to bow down before humanity. Therefore, Christians and Muslims often consider Melek Taus to be Satan. However, rather than being Satanic, Yazidism can be understood as a remnant of a pre-Islamic Middle Eastern Indo-European religion, and/or a ghulat Sufi movement founded by Shaykh Adi. In fact, there is no entity in Yazidism which represents evil in opposition to God; such dualism is rejected by Yazidis. | ||
In the Middle Ages, the [[Cathar]]s, practitioners of a dualistic religion, were accused of worshipping Satan by the Catholic Church. Pope Gregory IX stated in his work ''Vox in Rama'' that the Cathars believed that God had erred in casting [[Lucifer]] out of heaven and that Lucifer would return to reward his faithful. On the other hand, according to Catharism, the creator god of the material world worshipped by the Catholic Church is actually Satan. | |||
[[Wicca]] is a modern, syncretic [[Paganism|Neopagan]] religion, whose practitioners many Christians have incorrectly assumed to worship Satan. In actuality, Wiccans do not believe in the existence of Satan or any analogous figure and have repeatedly and emphatically rejected the notion that they venerate such an entity. | |||
The [[cult]] of the skeletal figure of [[Santa Muerte]], which has grown exponentially in Mexico, has been denounced by the Catholic Church as Devil-worship. However, devotees of Santa Muerte view her as an [[angel]] of death created by God, and many of them identify as Catholic. | |||
[[ | ==See also== | ||
* [[The Devil]] | |||
* [[Lucifer]] | |||
[[Category:Deities]] | [[Category:Deities]] | ||
[[Category:Featured Articles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:28, 19 December 2024

Satan, also known as The Devil is an entity in the Abrahamic religions that seduces humans into sin or falsehood. In Judaism, Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the yetzer hara, or "evil inclination."
In Christianity and Islam, he is usually seen as a fallen angel that has rebelled against God, who nevertheless allows him temporary power over the fallen world and a host of demons.
Satan in Judaism
The original Hebrew term śāṭān (Hebrew: שָׂטָן) is a generic noun meaning "accuser" or "adversary", which is used throughout the Bible to refer to ordinary human adversaries, as well as a specific supernatural entity. The word is derived from a verb meaning primarily "to obstruct, oppose". When it is used without the definite article (simply satan), the word can refer to any accuser, but when it is used with the definite article (ha-satan), it usually refers specifically to the heavenly accuser: the satan.
The word with the definite article Ha-Satan (Hebrew: הַשָּׂטָן) occurs 17 times in the Masoretic Text, in two books of the Hebrew Bible: Job ch. 1–2 (14×) and Zechariah 3:1–2 (3×). A figure known as ha-satan ("the satan") first appears in the Tanakh as a heavenly prosecutor, a member of the sons of God subordinate to Yahweh, who prosecutes the nation of Judah in the heavenly court and tests the loyalty of Yahweh's followers. During the intertestamental period, possibly due to influence from the Zoroastrian figure of Angra Mainyu, ha-satan developed into a malevolent entity with abhorrent qualities in dualistic opposition to God. In the apocryphal Book of Jubilees, Yahweh grants ha-satan (referred to as Mastema) authority over a group of fallen angels, or their offspring, to tempt humans to sin and punish them.
The Second Book of Enoch, also called the Slavonic Book of Enoch, contains references to a Watcher called Satanael. It is a pseudepigraphic text of an uncertain date and unknown authorship. The text describes Satanael as being the prince of the Grigori who was cast out of heaven and an evil spirit who knew the difference between what was "righteous" and "sinful". In the Book of Wisdom, the devil is taken to be the being who brought death into the world, but originally the culprit was recognized as Cain. The name Samael, which is used in reference to one of the fallen angels, later became a common name for Satan in Jewish Midrash and Kabbalah.
Modern beliefs
Each modern sect of Judaism has its own interpretation of Satan's identity. Conservative Judaism generally rejects the Talmudic interpretation of Satan as a metaphor for the yetzer hara, and regard him as a literal agent of God. Orthodox Judaism, on the other hand, outwardly embraces Talmudic teachings on Satan, and involves Satan in religious life far more inclusively than other sects. Satan is mentioned explicitly in some daily prayers, including during Shacharit and certain post-meal benedictions, as described in Talmud and the Jewish Code of Law. In Reform Judaism, Satan is generally seen in his Talmudic role as a metaphor for the yetzer hara and the symbolic representation of innate human qualities such as selfishness.
Satan in Christianity
The Book of Revelation represents Satan as the supernatural ruler of the Roman Empire and the ultimate cause of all evil in the world. In Revelation 2:9–10, as part of the letter to the church at Smyrna, John of Patmos refers to the Jews of Smyrna as "a synagogue of Satan" and warns that "the Devil is about to cast some of you into prison as a test, and for ten days you will have affliction." In Revelation 2:13–14, in the letter to the church of Pergamum, John warns that Satan lives among the members of the congregation and declares that "Satan's throne" is in their midst. Pergamum was the capital of the Roman Province of Asia and "Satan's throne" may be referring to the monumental Pergamon Altar in the city, which was dedicated to the Greek god Zeus, or to a temple dedicated to the Roman emperor Augustus.
In Revelation 20:1–3, Satan is bound with a chain and hurled into the Abyss, where he is imprisoned for one thousand years. In Revelation 20:7–10, he is set free and gathers his armies along with Gog and Magog to wage war against the righteous, but is defeated with fire from Heaven, and cast into the lake of fire. Some Christians associate Satan with the number 666, which Revelation 13:18 describes as the Number of the Beast. However, the beast mentioned in Revelation 13 is not Satan, and the use of 666 in the Book of Revelation has been interpreted as a reference to the Roman Emperor Nero, as 666 is the numeric value of his name in Hebrew.
The early English settlers of North America, especially the Puritans of New England, believed that Satan "visibly and palpably" reigned in the New World. John Winthrop claimed that the Devil made rebellious Puritan women give birth to stillborn monsters with claws, sharp horns, and "on each foot three claws, like a young fowl." Cotton Mather wrote that devils swarmed around Puritan settlements "like the frogs of Egypt". The Puritans believed that the Native Americans were worshippers of Satan and described them as "children of the Devil." Some settlers claimed to have seen Satan himself appear in the flesh at native ceremonies.
Satan in Islam
The Arabic equivalent of the word Satan is Shaitan (شيطان, from the triliteral root š-ṭ-n شطن). The word itself is an adjective (meaning "astray" or "distant", sometimes translated as "devil") that can be applied to both man ("al-ins", الإنس) and al-jinn (الجن), but it is also used in reference to Satan in particular. In the Quran, Satan's name is Iblis (Arabic pronunciation: [ˈibliːs]), probably a derivative of the Greek word diabolos. Muslims do not regard Satan as the cause of evil, but as a tempter, who takes advantage of humans' inclinations toward self-centeredness.
The primary characteristic of Satan, aside from his hubris and despair, is his ability to cast evil suggestions (waswās) into men and women. In the Quran, 15:45 states that Satan has no influence over the righteous, but that those who fall in error are under his power. 7:156 implies that those who obey God's laws are immune to the temptations of Satan. 56:79 warns that Satan tries to keep Muslims from reading the Quran and 16:98–100 recommends reciting the Quran as an antidote against Satan. 35:6 refers to Satan as the enemy of humanity and 36:60 forbids humans from worshipping him. In the Quranic retelling of the story of Job, Job knows that Satan is the one tormenting him.
During the first two centuries of Islam, Muslims almost unanimously accepted the traditional story known as the Satanic Verses as true. According to this narrative, Muhammad was told by Satan to add words to the Quran which would allow Muslims to pray for the intercession of pagan goddesses. He mistook the words of Satan for divine inspiration. Modern Muslims almost universally reject this story as heretical, as it calls the integrity of the Quran into question.
On the third day of the Hajj, Muslim pilgrims to Mecca throw seven stones at a pillar known as the Jamrah al-’Aqabah, symbolizing the stoning of the Devil. This ritual is based on the Islamic tradition that, when God ordered Abraham to sacrifice his son Ishmael, Satan tempted him three times not to do it, and, each time, Abraham responded by throwing seven stones at him.
Occult correspondences
In the hierarchy of Hell, Satan is the demon prince of the Deluders, the 5th degree of diabolical spirits. In this context, he is connected astrologically with the planet Mars.
In Kabbalah, Satan (alongside Moloch) is the demon ruler over the qlippoth of Thaumiel on the Tree of Death.
Satanism

Theistic Satanism
Theistic Satanism, commonly referred to as "devil worship", views Satan as a deity, whom individuals may supplicate to. It consists of loosely affiliated or independent groups and cabals, which all agree that Satan is a real entity.
The Afro-Brazilian religion of Quimbanda regards itself as worshipping the Devil and other spirits called exús that, while not inherently evil, are similar to demons.
Atheistic Satanism
Atheistic Satanism, as practiced by the Satanic Temple and by followers of LaVeyan Satanism, holds that Satan does not exist as a literal anthropomorphic entity, but rather as a symbol of a cosmos which Satanists perceive to be permeated and motivated by a force that has been given many names by humans over the course of time. In this religion, "Satan" is not viewed or depicted as a hubristic, irrational, and fraudulent creature, but rather is revered with Prometheus-like attributes, symbolizing liberty and individual empowerment.
To adherents, he also serves as a conceptual framework and an external metaphorical projection of the Satanist's highest personal potential. In his essay "Satanism: The Feared Religion", the current High Priest of the Church of Satan, Peter H. Gilmore, further expounds that "...Satan is a symbol of Man living as his prideful, carnal nature dictates. The reality behind Satan is simply the dark evolutionary force of entropy that permeates all of nature and provides the drive for survival and propagation inherent in all living things. Satan is not a conscious entity to be worshiped, rather a reservoir of power inside each human to be tapped at will".
LaVeyan Satanists embrace the original etymological meaning of the word "Satan" (Hebrew: שָּׂטָן satan, meaning "adversary"). According to Peter H. Gilmore, "The Church of Satan has chosen Satan as its primary symbol because in Hebrew it means adversary, opposer, one to accuse or question. We see ourselves as being these Satans; the adversaries, opposers and accusers of all spiritual belief systems that would try to hamper enjoyment of our life as a human being."
Post-LaVeyan Satanists, like the adherents of the Satanic Temple, argue that the human animal has a natural altruistic and communal tendency, and frame Satan as a figure of struggle against injustice and activism. They also believe in bodily autonomy, that personal beliefs should conform to science and inspire nobility, and that people should atone for their mistakes.
Accusations of Satan Worship
The main deity in the tentatively Indo-European pantheon of the Yazidis, Melek Taus, is similar to the devil in Christian and Islamic traditions, as he refused to bow down before humanity. Therefore, Christians and Muslims often consider Melek Taus to be Satan. However, rather than being Satanic, Yazidism can be understood as a remnant of a pre-Islamic Middle Eastern Indo-European religion, and/or a ghulat Sufi movement founded by Shaykh Adi. In fact, there is no entity in Yazidism which represents evil in opposition to God; such dualism is rejected by Yazidis.
In the Middle Ages, the Cathars, practitioners of a dualistic religion, were accused of worshipping Satan by the Catholic Church. Pope Gregory IX stated in his work Vox in Rama that the Cathars believed that God had erred in casting Lucifer out of heaven and that Lucifer would return to reward his faithful. On the other hand, according to Catharism, the creator god of the material world worshipped by the Catholic Church is actually Satan.
Wicca is a modern, syncretic Neopagan religion, whose practitioners many Christians have incorrectly assumed to worship Satan. In actuality, Wiccans do not believe in the existence of Satan or any analogous figure and have repeatedly and emphatically rejected the notion that they venerate such an entity.
The cult of the skeletal figure of Santa Muerte, which has grown exponentially in Mexico, has been denounced by the Catholic Church as Devil-worship. However, devotees of Santa Muerte view her as an angel of death created by God, and many of them identify as Catholic.